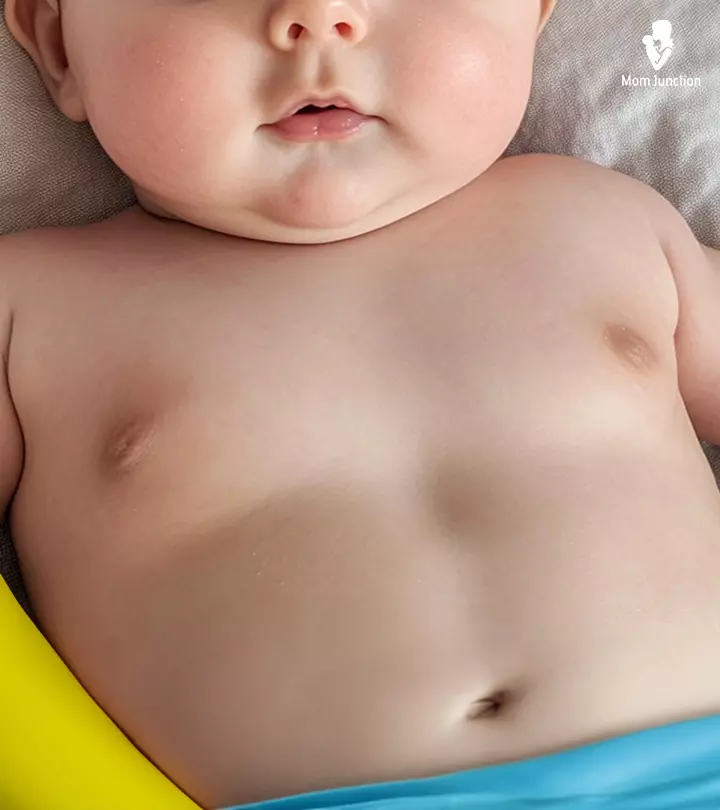
Image: Midjourney/ MomJunction Design Team
Enlargements or lumps in the baby’s breast are common among newborns and are usually harmless. The condition may result in visible lumps under the nipple in one or both breasts, and it can affect boys and girls alike. In most cases, such breast lumps subside without requiring treatment. However, you may consult a pediatrician to rule out any underlying issues.

Keep reading the post to learn about the causes of baby breast lumps, when they disappear, and when to consult a doctor.
Key Pointers
- Breast lumps in babies can be caused by maternal hormonal shifts, certain medicines, or congenital malformations.
- In most cases, it subsides after days or weeks with proper treatment.
- Do not squeeze or pinch the baby’s breast lumps.
- Consult a neonatologist if you observe nodules or pus seeping from the baby’s breast.
Causes Of Breast Lumps And Enlargement In Babies
Board-certified diplomate of the Philippine Pediatric Society, Dr. Maria Carmela Villania-Mamauag, opines, “Breast lumps in infants are typically caused by maternal hormones, such as prolactin or estrogen, especially if they appear within the first two weeks after birth in males or between 2 to 6 months in females. If the lumps are not red, tender, rapidly enlarging, or associated with other symptoms, they are generally self-limiting and do not require investigation or treatment.”
The following factors may lead to the formation of lumps in the baby’s breast.
1. Maternal hormonal changes

During pregnancy, there is an increase in the levels of estrogeniHormone responsible for the development of reproductive system and sexual characteristics. hormone, which could pass into the baby inside the womb (1). The hormone’s effects could persist after birth, and some babies may develop breast lumps a few days after birth. A mother will also produce high levels of prolactin hormone, which enables milk production in her. Prolactin may also pass into the baby inside the womb, causing breast lumps after birth. Some babies may even secrete a bit of breast milk, also called Neonatal milk or galactorrhea, in which milk is secreted from a baby’s breasts., due to the effects of the hormone (2).
Maternal hormones are the most common cause of baby breast lumps. Studies suggest that maternal estrogen usually causes some degree of breast enlargement in nearly 70% of newborns (3).
 Trivia
Trivia2. Isolated premature thelarche
Premature thelarche is the condition where a girl shows breast development before the age of eight years (4). Breast enlargement can occur even without early puberty, giving the appearance of breast development in infants and toddlers (5).
Isolated premature thelarche usually occurs due to maternal hormones. Some rare causes include ovarian cysts and precocious puberty.
3. Medications
If the mother is exposed to certain medications during pregnancy, it may cause a surge in hormones (6). These hormones could pass into the baby and lead to the formation of breast lumps in newborns (1). A baby or a child under eight years of age may develop breast lumps or early breast development due to exposure to some products containing estrogen, such as estrogen sprays, estrogen in cosmetics, and lavender and tea tree oil (7).
4. Infections and disorders

In rare cases, infections and disorders may lead to the formation of breast lumps in babies. Babies who experience endocrine disordersiendocrine disorders Definition: A list of endocrine disorders caused by improper functioning. , such as thyroid disorders, may experience premature thelarche with precocious puberty (8). Some less common causes of lumps in the baby’s breast include problems with the central nervous system, genetic disorders, and breast tumors (7).
Neonatal mastitis (infection of the breasts) may cause swelling beneath the nipples (10). The causative agents of the infection are similar to those seen in mastitis in adults. Staphylococcus and Streptococcus bacteria are some of the leading causes (3). A swollen breast in newborn due to a bacterial infection will generally display other signs, such as fever, fussiness, and lethargy.
 Research finds
Research finds5. Congenital deformities
Some babies may experience congenitaliCondition that is present at birth and may be inherited or acquired. deformities in the nipple or the tissues of the chest (11). It may cause the appearance of enlarged breasts. In rare cases, the baby might be born with a benign breast tumor or vascular (blood vessel-related) deformations (12), which may render the breast a swollen appearance.
Pediatrician Dr. Raashid Hamid opines, “While extremely rare, breast lumps in infants can sometimes be linked to congenital conditions or hormonal disorders. If there’s a family history of such conditions or if the lump is accompanied by other unusual symptoms, a thorough medical evaluation is recommended.”
When Do Breast Lumps In A Baby Go Away?
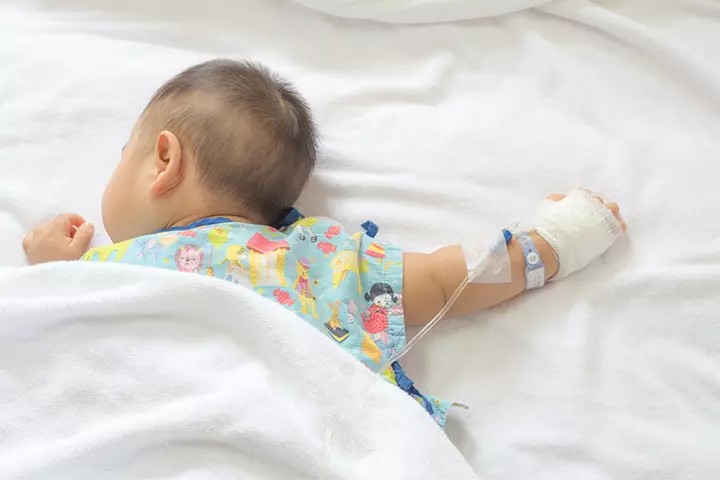
Breast lumps due to maternal hormones usually subside within two weeks (1). The reduction of breast lumps due to other causes may depend on several factors, such as the type of cause, the severity of the cause, and if the condition requires treatment. In most cases, the appropriate treatment or management causes the breast lumps to go away within days to weeks.
Certain causes, such as congenital deformitiesicongenital deformities Definition: Structural or functional differences in a newborn that have occurred before birth. and severe endocrine disorders, may require extensive long-term treatment. You may speak to a pediatrician to determine the treatment and the prognosis of the condition.
When To Consult The Doctor?
Dr. Lauren M Chiriboga, a general pediatrician from Nicklaus Children’s Hospital in Miami, Florida, says, “Breast lumps in babies typically do not require treatment. Their evaluation and possible treatment may be warranted in the case of concurrent symptoms, such as bleeding or discharge from the nipple, redness or warmth of the overlying skin, fever, or severe asymmetry of the nipples or breast area.”
A pediatrician is likely to assess the presence of any breast anomalies at birth and during a routine check-up.
In the following cases, you may consult a pediatrician for breast lump evaluation in infants (13).
- The lumps do not subside after two weeks.
- The lumps constantly enlarge.
- You notice redness on the swollen breast.
- You notice nodules on the enlarged breasts.
- The nipples ooze pus.
- The baby itches the breast lump often.
- The baby has signs of infection, such as fever.
- You notice persistent crying, fussiness, and loss of appetite.
The doctor may advise tests, such as blood tests, mammographyiAn imaging technique that examines breasts for cancer and other diseases using X-ray imaging. , and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), depending on the severity of signs and symptoms (13). Breast lumps due to maternal hormones do not require any treatment. Other causes of breast enlargement may require appropriate treatment.

Dos And Don’ts With Breast Lumps In Babies
Keep in mind the following points if your baby has enlarged breasts.
- Never pinch the lumps as it may cause irritation and infection.
- Do not squeeze the milky liquid or the Witch’s milk. Let the secretion subside naturally.
- Clean any secretion from breasts with a moist, soft cloth.
- Keep the nipple and the surrounding skin clean.
- Maintain the usual feeding pattern for the baby.
 Quick fact
Quick fact
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are breast buds in babies?
Tiny, disc-shaped lumps under the areola or nipple of the baby are called breast buds. Any lumps under a baby’s breast are considered breast buds until proven otherwise (13).
2. Is it normal for babies to have lumps under nipples?
Both male and female newborn babies can have breast lumps due to exposure to maternal estrogen hormones. This usually disappears within a few weeks after birth (16).
“Breast budding in baby boys and girls is normal. Breast buds may not be present in all babies; however, most babies will have changes in the texture of the tissue under the nipple during the first six to 18 months of life, which is normal and typically does not require any special evaluation or treatment apart from the regular well-child visits,” Dr. Chiriboga suggests.
3. At what age do breast buds appear?
Usually, breast buds appear in young girls around the age of nine, before puberty. However, it is possible to appear by six in some girls (16).
4. What signs and symptoms may accompany breast buds in babies?
“Breast buds in babies are usually an isolated finding that do not present with any other symptoms,” opines Dr. Chiriboga.
5. Can lumps in a baby’s breast cause pain or discomfort?
Breast lumps caused by factors other than maternal hormones, such as an infection, may cause pain and discomfort in babies. Contact a pediatrician if you notice symptoms such as red and swollen breasts, fever, and discharge from nipples.
6. Are there any home remedies for lumps in a baby’s breast?
There are no recommended home remedies for lumps in a baby’s breast. It is best to seek medical attention from a pediatrician to diagnose and treat the underlying cause of the lump.
7. How often should I check my baby’s breasts for lumps?
It is not necessary to check for lumps in the baby’s breast regularly. However, if you notice any unusual changes or lumps while bathing or dressing your baby, consult your pediatrician.
Lumps in baby’s breasts are mostly caused due to maternal hormonal changes and are seldom harmful. They usually subside on their own without treatment in a few weeks. However, if lumps occur due to infections or congenital anomalies, they may require specialized treatment. Look out for any changes in lump size, discharges, or signs of infections such as fever and loss of appetite. Avoid pressing the affected area or squeezing out any milky secretion, and keep the surrounding skin clean. Consult a pediatrician if you suspect any abnormality.
Infographic: Other Conditions Causing Breast Swelling In Babies
Breast lumps and mild swelling due to maternal hormones are often self-resolving in newborns. Nevertheless, there could be more serious underlying causes for breast enlargement and lumps in neonatesiNewborn less than 4 weeks old. , some of which are discussed in this infographic.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
If you observe that your child’s chest is swollen it may cause you concern. Watch this video to better understand why this may be happening and how you should proceed.
References
1. Hormonal effects in newborns; U.S. National Library of Medicine
2. T. Forbes, Witch’s Milk and Witches’ Marks; Semantic Scholar
3. V Raveenthiran, Neonatal Mastauxe (Breast Enlargement of the Newborn); Journal of Neonatal Surgery; NCBI
4. Prithi R Inamdar et al., Isolated premature thelarche: A normal growth variant; Journal of the Scientific Society
5. Dr Yuranga Weerakkody et al., Premature thelarche; Radiopaedia
6. Pregnancy, breastfeeding and fertility while taking or using oestrogen tablets, patches, gel and spray; NHS
7. Breast Symptoms In A Child; American Academy of Pediatrics; Healthychildren.org
8. Precocious Puberty; Stanford’s Children Health
9. Ayman Al-Jazaeri et al., Unilateral breast mass in an infant: a rare presentation of spontaneously regressing myofibromatosis; NCBI
10. Nahar AL Ruwaili and Dennis Scolnik, Neonatal Mastitis: Controversies in Management; Journal of Clinical Neonatology; NCBI
11. Breast and Chest Wall Disorders; Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia
12. Harriet Bagnal Hinen et al., Childhood Vascular Tumors; Frontiers in Pediatrics
13. Breast Symptoms-Child; Seattle Children’s Hospital
14. Breast Lumps; Radiological Society of North America
15. 14-04: Neonatal Milk Production (Witch’s Milk); Access Emergency Medicine
16. Breast Lump; MedlinePlus
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Dur Afshar Agha
- Dr. Raashid Hamid is a consultant in the department of Pediatric Surgery at GMC hospital and associate professor of Pediatric and Neonatal Surgery at SKIMS, Jammu & Kashmir, India. He has four years of experience and specializes in general surgeries, including appendectomy, cholecystectomy, and exploratory laparotomy.
 Dr. Raashid Hamid is a consultant in the department of Pediatric Surgery at GMC hospital and associate professor of Pediatric and Neonatal Surgery at SKIMS, Jammu & Kashmir, India. He has four years of experience and specializes in general surgeries, including appendectomy, cholecystectomy, and exploratory laparotomy.
Dr. Raashid Hamid is a consultant in the department of Pediatric Surgery at GMC hospital and associate professor of Pediatric and Neonatal Surgery at SKIMS, Jammu & Kashmir, India. He has four years of experience and specializes in general surgeries, including appendectomy, cholecystectomy, and exploratory laparotomy. - Dr. Maria Carmela Villania-Mamauag is a board certified diplomate of the Philippine Pediatric Society with a degree of Doctor of Medicine from Our Lady of Fatima University, Valenzuela City and a Bachelor in Science in Psychology from Saint Louis University, Baguio City which was augmented by a year of Bachelor in Science in Family Life and Child development at the University of the Philippines, Diliman, Quezon City.
 Dr. Maria Carmela Villania-Mamauag is a board certified diplomate of the Philippine Pediatric Society with a degree of Doctor of Medicine from Our Lady of Fatima University, Valenzuela City and a Bachelor in Science in Psychology from Saint Louis University, Baguio City which was augmented by a year of Bachelor in Science in Family Life and Child development at the University of the Philippines, Diliman, Quezon City.
Dr. Maria Carmela Villania-Mamauag is a board certified diplomate of the Philippine Pediatric Society with a degree of Doctor of Medicine from Our Lady of Fatima University, Valenzuela City and a Bachelor in Science in Psychology from Saint Louis University, Baguio City which was augmented by a year of Bachelor in Science in Family Life and Child development at the University of the Philippines, Diliman, Quezon City. - Dr. Lauren Chiriboga did medicine at Florida International University Herbert Wertheim College of Medicine in Miami and a residency in pediatrics at Nicklaus Children’s Hospital. With over five years of experience as a pediatrician, Dr. Chiriboga currently works with Nicklaus Children’s Pediatric Care Centers.
 Dr. Lauren Chiriboga did medicine at Florida International University Herbert Wertheim College of Medicine in Miami and a residency in pediatrics at Nicklaus Children’s Hospital. With over five years of experience as a pediatrician, Dr. Chiriboga currently works with Nicklaus Children’s Pediatric Care Centers.
Dr. Lauren Chiriboga did medicine at Florida International University Herbert Wertheim College of Medicine in Miami and a residency in pediatrics at Nicklaus Children’s Hospital. With over five years of experience as a pediatrician, Dr. Chiriboga currently works with Nicklaus Children’s Pediatric Care Centers.
Read full bio of Dr. Ritika Shah
Read full bio of Swati Patwal
Read full bio of Ghazia Shah