Image: Shutterstock
Autism is a neurological condition that affects how a child’s brain processes social interactions and behaviors. Some early indicators of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in children include minimal eye contact, restricted body language, and repetitive actions or speech patterns (1). As a result, it may be difficult for a child with ASD to learn skills required for everyday functioning that might eventually affect their behavior, communication, and the ability to understand social cues and social-emotional skills. Since ASD is a spectrum, each child may display a unique combination of strengths and challenges (2). Read on about the types, causes, risk factors, treatment, and management of autism spectrum disorder in children.
Key Pointers
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in children can be of five types.
- Maternal exposure to toxins, genetic inheritance, and other underlying factors increase the risk of this condition.
- Delay of speech, repeated movements, and problems with understanding words are some of the common symptoms.
- Diagnosis generally involves understanding the child’s development and behavioral pattern.
How Common Is Autism Spectrum Disorder?
According to estimates made by the CDC’s Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, about one in 36 children are diagnosed with ASD.
The disorder is more common in boys than girls and is prevalent in people of all racial, socioeconomic, and ethnic backgrounds (3).
The graph shows the increase in the percentage of children with autism in the US through the years 2004 to 2026. The percentage of children with ASD increased through the years, with the curve being stagnant in the years 2014 and 2016 (4).

Autism prevelance rate in the US
Source: Centers for Disease Control and PreventionTypes Of Autism Spectrum Disorder
There are five main types of autism spectrum disorder (5).
1. Level 1 Autism Spectrum Disorder
Although it was earlier called Asperger’s syndrome (most people are still familiar with this name), it has been reclassified as level 1 autism spectrum disorder by the American Psychiatric Association’s DSM-5 diagnostic manual. Children with level 1 autism spectrum disorder often demonstrate strong language skills and above-average intelligence, but may find social communication challenging.
Some common characteristics of a child with level 1 ASD include:
- Difficulty adapting to changes and maintaining rigid thought patterns
- Issues with organization and planning due to executive functioning deficits
- Trouble shifting focus from one activity to another
- Speaking in a monotone voice with limited emotional expression in speech
- Challenges in social interactions make it harder to build relationships with peers
2. Rett syndrome
It is a rare neurodevelopmental disorder in infants, primarily girls. A global prevalence study by multiple researchers indicated that Rett syndrome is diagnosed among 7.1 cases per 100,000 females (6). This syndrome affects almost every aspect of life as it is characterized by loss of coordination, breathing problems, and communication and speech problems (7).
Common symptoms of Rett syndrome include:
- Difficulties with verbal communication, making it hard to express needs and emotions
- Diminished control over movement and coordination, affecting balance and daily activities
- Breathing abnormalities, such as inconsistent breathing patterns
 Point to consider
Point to consider3. Childhood disintegrative disorder (CDD)

Childhood disintegrative disorder is also known as Heller’s syndrome or disintegrative psychosis. It is one of the childhood disorders that cause development problems in language, motor skills, toileting skills, or social function. Children with childhood disintegrative disorder (CDD) usually follow a typical developmental path until they reach three to ten years old, at which point they begin to lose previously acquired skills. Research also shows that boys are far more likely to be diagnosed with CDD than girls, with males accounting for nine out of ten cases.
A child with childhood disintegrative disorder may experience a regression in various skills, including:
- Previously learned toileting habits
- Language development and vocabulary
- Certain motor functions
- Social interactions and adaptive behaviors
4. Kanner’s syndrome
It is described as a classic autistic disorder. Children with this syndrome appear intelligent and alert but have a few underlying problems.
Children with Kanner’s syndrome may seem bright and attentive, yet they exhibit specific traits associated with the condition, including:
- Difficulty forming emotional bonds with others
- Challenges in communication and social interactions
- Intense fixation on handling certain objects
- Uncontrolled or repetitive speech patterns
- Strong rote memory and visuospatial abilities but struggles in other areas of learning
5. Pervasive developmental disorder – not otherwise specified (PDD-NOS).
This is a mild type of autism disorder with varying symptoms, the most common of which include difficulties in developing social and language skills. Mobility and motor skill development may also be slower in some children. Often referred to as ‘subthreshold autism,’ this condition describes individuals who exhibit some but not all traits of autism. Careful observation can help identify this type of autism by pinpointing challenges in areas like social engagement and communication, as well as delays in certain developmental milestones.
Is Rett Syndrome An ASD?
Rett syndrome is a type of autism that usually occurs in girls. Rett syndrome is caused by a mutation in the MECP2 gene on the X chromosome and does not occur at birth. The similarities between Rett syndrome and ASD include symptoms such as repetitive behaviors, anxiety, and seizures.
Generally, children diagnosed with Rett syndrome show temporary atypical social behavior, while those with ASD may show atypical behavior for a longer period. Also, children with Rett syndrome may have more severe movement problems than those with ASD (7).
ASD Symptoms In Children
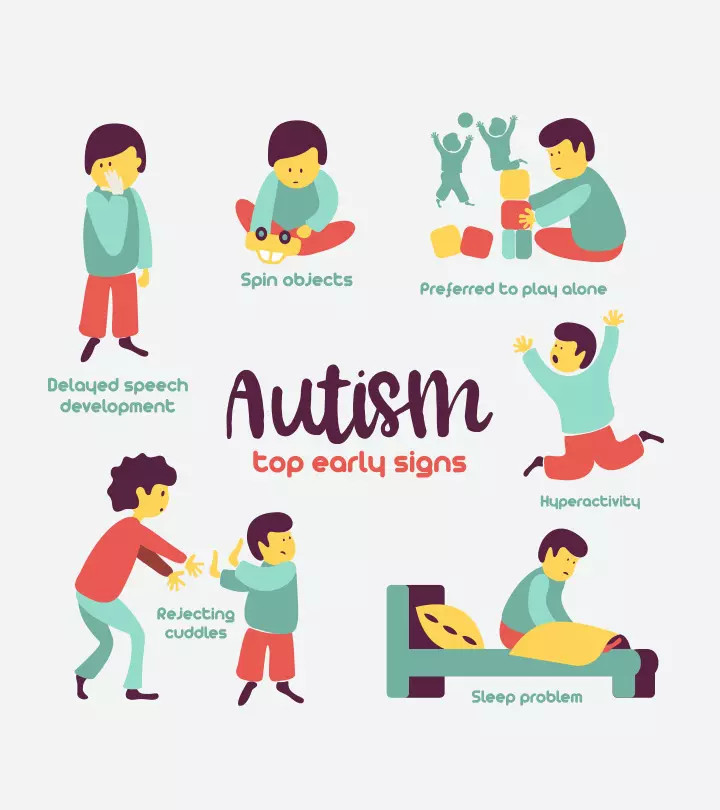
The following are some signs and symptoms that can be noticed in children with ASD (8).
- Reduced eye contact and lack of facial expressions
- Inability to respond to their name
- Preference to stay alone

- Resistance to holding or cuddling
- Speech and developmental delays
- Problems starting conversations and interacting with others.
- Abnormal tone while speaking, such as speaking like a robot or speaking to the tune of a song
- Inability to express themselves and understand people’s expressions.
- Difficulty understanding simple words, phrases, sentences, and questions and lack of cognitive flexibility
- Repetition of movements, such as rocking, spinning, or hand flapping
- Problems with coordination, such as toe walking and stiff body
- Sensory sensitivities to light touch or sounds
- Peculiar food preferences
- Struggles to recognize social signals
- Finds it challenging to interpret and use body language, such as turning away while speaking to someone (1).
 Quick fact
Quick factCauses And Risk Factors For ASD In Children
Exact causes for autism spectrum disorder are not known. However, experts believe that it could be a combination of environmental and genetic factors. The following factors could put a child at a higher risk for ASD (1) (9).
- Exposure to toxins, air pollution, or certain pesticides before or after birth (10)
- Infections before birth and low birth weight
- Having an older parent or a sibling with ASD. Studies have shown that autism tends to run in families, meaning that genetics play a major role in its development. A review of seven twin studies found that inherited factors contribute to about 60% to 90% of the risk of autism. This means that if one child in a family has autism, the chances of their sibling also having autism are higher compared to families without a history of the condition (10).
- Viral infections in children such as meningitisiInflammation of the protective membranes and fluid that surround the brain and spinal cord or encephalitisiA condition characterized by brain swelling due to infections, insect bites, or autoimmune conditions. , which lead to brain damage.
- Various genetic conditions are said to be involved in autism spectrum disorder. For some children, autism spectrum disorder can be due to Rett syndrome or fragile X syndrome, and for others, it could be Down syndromeiA genetic condition where a person has an extra chromosome apparent through facial features, and speech and language problems .

Complications Of ASD In Children
ASD can sometimes lead to the following complications (11).
- Fragile X syndrome
- Intellectual disability
- Tuberous sclerosisiA rare genetic condition that may cause non-cancerous tumors in many parts of the body
- Social and emotional problems
 Did you know?
Did you know?Diagnosis And Tests
The diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder can be tricky as no specific medical tests exist. Therefore, mental health professionals observe the child’s development pattern and behavior to conclude the diagnosis.
There are specific questionnaires for screening which your pediatrician normally does at routine well-baby visits at 18 months and 24 months of age. However, if you observe any discrepancy or abnormal behavior in your child at a younger age, bring it to your doctor’s attention so that the baby can be appropriately evaluated.
Children who show symptoms of developmental problems during well-child check-ups are further evaluated by experts such as a developmental pediatrician, a pediatric psychologist or psychiatrist, a neuropsychologist, and a speech-language pathologist. In some cases, blood tests and hearing tests may also be performed to rule out other disorders (1) (12).
Management And Treatment Of ASD In Children
The symptoms of ASD can be managed and treated using the following approaches (13).
- Behavior and communication approaches: These approaches help the child gain structure, organize themselves, and improve their social, communication, and movement skills. They include behavior therapy such as applied behavior analysis (ABA) and speech and language therapy. A small-scale research conducted on 60 boys aged four to 11, split into two equal groups, found that a behavioral analysis program greatly improved the social and communication abilities of institutionalized children, positively impacting their everyday lives (14).
- Dietary approaches: These involve removing particular types of foods from the child’s diet and replacing them with vitamins and supplements. A review of 26 studies explored different nutritional strategies for ASD, including casein-free diets and gluten-free, vitamins, minerals,omega-3 supplements, probiotics, and prebiotics. The studies varied in methodology, participant numbers, and outcome assessments. Overall, results indicated that some nutritional interventions positively influenced ASD symptoms, such as enhancing social interactions, communication skills, and reducing hyperactivity and repetitive behaviors (15).
- Medications: Medications prescribed by a healthcare professional may help regulate their energy, focus, or any form of behavioral activity or self-injury. It may not cure the core symptoms but helps in managing them.
- Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) treatments: Some parents may use treatment methods that fall outside the regular approaches. These may include a particular diet, chelationiA therapy that involves the use of medications to eliminate heavy metals from the body , or mind-body medicine. Always consult a doctor before trying any CAM treatments.
Recalling how she discovered the food preferences of her child with autism spectrum disorder, Farjana Akhtar, a mother, says, “As for my son in starting, I could not understand what kind of food he liked. So I offered him various types of food, and then I understood that he liked to eat spicy food. He enjoys it most when I hug and kiss him (i).”
Prevention Of ASD In Children
There is no specific way to prevent ASD in children as the exact cause of the disorder is not known. Mental health professionals state that ASD is not related to the way a child is raised. They also believe that any vaccination taken during childhood has no role in the development of ASD.
Therefore, the best approach to help a child with ASD is to diagnose and treat the symptoms early. This will help enhance the child’s development and improve their quality of life (9).
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is ASD permanent?
ASD is a lifelong condition (1). However, a new study claims that early intervention can resolve the symptoms of ASD as the child grows older (16). Many interventions assist children in learning many life skills. Engaging the child in therapy could benefit the child throughout their life.
2. Is autism a learning disability?
Autism is not a learning disability. But the signs may overlap with that of learning disabilities. These signs may also impact a child’s problem-solving ability, knowledge of verbal or non-verbal cues, attention span, and communication skills, which might affect their learning abilities.
3. At what age does ASD appear in children?
A child might show symptoms of ASD between 12 months and three years. They may reach their developmental milestones late and stop developing new skills (17).
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in children is a developmental disorder that primarily impacts children’s social skills. Rett syndrome, Kanner’s syndrome, Level 1 ASD, Childhood Disintegrative Disorder (CDD), and PDD-NOS are the different types. The complications of ASD include Fragile X syndrome, Tuberous sclerosis, intellectual disability, and social and emotional problems. This disorder can be treated using dietary approaches, medications, CAM treatments, and behavior and communication approaches. Activities for kids with autism support their development and improve social skills. If you notice any abnormality in your child’s behavior, consult your doctor immediately and ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Infographic: Do Children With Autism Outperform Their Peers In Certain Skills?
Children with autism may have proficient skills in certain areas. Turning their talent in the right direction can do wonders. Although they face communication skills and socialization issues, most are blessed with gifted abilities. Go through the infographic to know the exceptional abilities of children with autism to identify and grow their special talents.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
Illustration: Autism Spectrum Disorder In Children: Types Symptoms & Causes

Image: Stable Diffusion/MomJunction Design Team
Raising a child with autism can be challenging, but it can also be incredibly rewarding. Explore how to best support and nurture your child with the help of this video.
Personal Experience: Source
MomJunction articles include first-hand experiences to provide you with better insights through real-life narratives. Here are the sources of personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. How to take care of an autism child.https://medium.com/@farjanalilaboti/how-to-take-care-of-an-autism-child-8dce8380739b
References
- Autism.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/autism - Autism Spectrum Disorder.
https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/autism-spectrum-disorders-asd - Data and Statistics on Autism Spectrum Disorder.
https://www.cdc.gov/autism/data-research/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/autism/data.html - Prevalence of Autism Increases by 10%, to 1 in 54 Children.
https://autismcenter.org/prevalence-autism-increases-10-1-54-children/ - What Are The 5 Types Of Autism.
https://www.integrityinc.org/what-are-the-5-types-of-autism/ - Petriti, Uarda, et al; Global Prevalence of Rett Syndrome: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.
https://systematicreviewsjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13643-023-02169-6#:~:text=The%20pooled%20prevalence%20estimate%20(random%20effects)%20was%207.1%20per%20100%2C000%20females - Rett Syndrome.
https://www.thetransmitter.org/spectrum/rett-syndromes-link-to-autism-explained/?fspec=1 - Signs and Symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorder;
https://www.cdc.gov/autism/signs-symptoms/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/autism/signs.html - Autism Spectrum Disorder In Children.
https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?ContentTypeID=90&ContentID=P02556 - What causes autism?
https://www.autismspeaks.org/what-causes-autism - Autism spectrum disorder.
https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/diseases-conditions/autism-spectrum-disorder - Screening for Autism Spectrum Disorder;
https://www.cdc.gov/autism/diagnosis/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/autism/screening.html - Treatment and Intervention for Autism Spectrum Disorder;
https://www.cdc.gov/autism/treatment/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/autism/treatment.html - Du, Geng, et al; The Effectiveness of Applied Behavior Analysis Program Training on Enhancing Autistic Children’S Emotional-social Skills.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11487924/ - Pancheva, Ruzha, et al; Therapeutic Diets and Supplementation: Exploring Their Impact on Autism Spectrum Disorders in Childhood – A Narrative Review of Recent Clinical Trials.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1750946724000278 - Early Autism May Not Last A Lifetime.
https://www.nih.gov/news-events/nih-research-matters/early-autism-may-not-last-lifetime - About Autism Spectrum Disorder;
https://www.cdc.gov/autism/about/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/autism/facts.html - Medical Conditions Associated With Autism
https://www.autismspeaks.org/medical-conditions-associated-autism
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Garima Garg Seth
Read full bio of Apoorva K
Read full bio of Dr. Ritika Shah
Read full bio of Vidya Tadapatri