
Image: Shutterstock

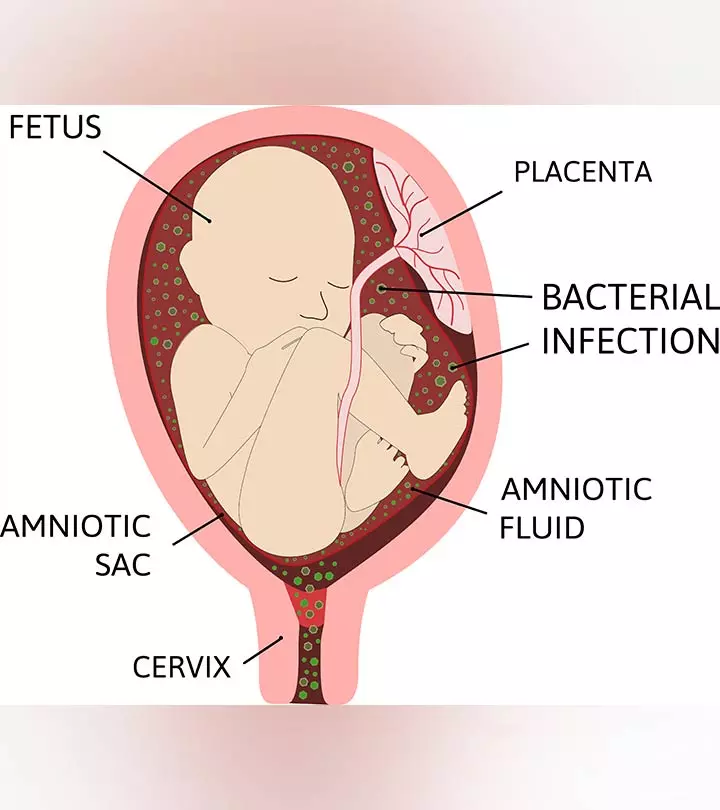
Chorioamnionitis, also known as intraamniotic infection, is a serious infection in pregnancy. It is characterized by the infection of the membranes that surround the fetus (chorion and amnion), the umbilical cord, and the amniotic fluid (1) (2).
The condition affects around 40-70% of women with premature delivery and two to four percent of women with full-term pregnancies, indicating it is more common in preterm deliveries (3). Read about the causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of chorioamnionitis in pregnant women.
Causes Of Chorioamnionitis
Chorioamnionitis is mostly caused by the bacteria moving up from the vagina and the cervix into the uterus. These bacteria are normally present in the vagina, but when the amniotic sac (water bag) breaks open prematurely, the bacteria travel upwards into the uterus and cause the infection (4). It may also be a complication of other invasive procedures such as amniocentesis or fetoscopy.
Symptoms Of Chorioamnionitis
Some women might not show any symptoms of chorioamnionitis, and the diagnosis can only happen when they experience early water breakage or preterm prelabour rupture of membranes (PPROM). The following symptoms may be seen in some other women (1) (3).
- High fever
- Abdominal pain and tenderness over the womb
- Tachycardia ( >100 heartbeats/minute)
- Fetal heart tachycardia ( >160 heartbeats/minute)
- Vaginal discharge
- Leukocytosis (
While it is normal to have increased vaginal discharge in pregnancy, you must consult your healthcare if it is accompanied by an unpleasant odor, greenish or yellowish discoloration, itchiness, soreness around the vagina, or pain while peeing.
Risk Factors For Chorioamnionitis
The following factors may increase a pregnant woman’s risk of developing chorioamnionitis (2) (5) (6)
- Smoking during pregnancy
- Alcohol or illicit drug abuse during pregnancy
- Sexually transmitted diseases such as trichomoniasis, chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, or HIV
- Group B strep infection
- Bacterial vaginosis
- History of urinary tract infections
- Short cervix
- Preterm prelabour rupture of membranes (PPROM)
- Preterm labor
The following complications during labor might also lead to chorioamnionitis.
- A long labor
- Takes longer than 24 hours for the woman to enter labor after the water breaks.
- Multiple internal examinations during labor
- The baby poops during labor (meconium), which enters into the amniotic fluid
Diagnosis For Chorioamnionitis
The diagnosis of chorioamnionitis is majorly based on the clinical signs and findings. If the clinical signs indicate a need, a sample of the amniotic fluid is extracted from the uterus by an ultrasound-guided needle aspiration technique. It is unsafe and impractical to take a sample of the membrane or amniotic fluid for testing unless there is an absolute need and the benefits outweigh the risks of the procedure (6).
Treatment For Chorioamnionitis
Chorioamnionitis can be detrimental to fetal health. However, diagnosing and timely intervention can help avoid complications. Prompt and aggressive antibiotic therapy substantially reduces the risks of harm to the baby and the mother.
Early antibiotics administration can reduce the risk of neonatal sepsis by more than 80%. Ampicillin is the most commonly prescribed antibiotic for chorioamnionitis. It is administered intravenously every four to six hours during labor and then a single dose post-delivery (6).
Complications Of Chorioamnionitis
Chorioamnionitis can lead to a serious blood infection, bacteremia in the mother (4). The infection refers to viable bacteria in the blood and may lead to premature birth.
It may also cause serious infections such as pneumonia, meningitis, brain damage, or fetal death (4).
Prevention Of Chorioamnionitis
The following tips can help prevent chorioamnionitis in pregnant women (1).
- Use plain water and soap to clean your genitals.
- Avoid scented soaps, bubble baths, shampoos, shower gels, vaginal deodorants, vaginal washes, douches, etc.,
- Consult your doctor if you experience the symptoms of a urinary tract infection.
- Minimizing the number of internal examinations or vaginal examinations can help prevent chorioamnionitis.
- Avoid smoking, alcohol consumption, and drug abuse.
- Speak to your healthcare provider if you experience abnormal or unusual vaginal discharge. You may be prescribed antibiotics early in pregnancy if you experience water breakage to help avoid chorioamnionitis (4).
- Do not skip any antenatal appointments.
- If you believe that you may have STIs, you must get tested.
- Get screened for infections such as bacterial vaginosis, group B streptococcal infection as advised by the doctor.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the long-term outlook for people with chorioamnionitis?
Timely treatment can mean an excellent prognosis for both the mother and the child. However, according to research, chorioamnionitis in the current pregnancy may marginally increase the woman’s risk of developing it in subsequent pregnancies.
Six percent of women who have had chorioamnionitis in the first pregnancy developed it again in the second pregnancy, and two percent of women without a previous history developed it in the second pregnancy (8).
2. Can chorioamnionitis cause cerebral palsy?
Yes, chorioamnionitis increases the risk of cerebral palsy in full-term infants four times (9).
3. What is the difference between chorioamnionitis and endometritis?
Chorioamnionitis is the infection of the membranes surrounding the fetus, while endometritis is the inflammation or irritation of the uterine lining (10).
Chorioamnionitis is a bacterial infection of fetal membranes, including amnion and chorion. The chemical substance released in response to this infection can cause premature labor or prolonged labor. You may contact your healthcare provider if you develop any symptoms of chorioamnionitis, such as abdominal pain: fever, or tachycardia. Treating urinary symptoms on time and avoiding urogenital infections, and maintaining hygiene measures could reduce the risk of developing intraamniotic infections. In addition, follow antibiotic therapy as prescribed to reduce the risk of pregnancy and neonatal complications.
Key Pointers
- Chorioamnionitis occurs when the amniotic sac breaks open, and the bacteria from the vagina and cervix move into the uterus.
- Some women may not have any symptoms, while others may experience high fever, abdominal pain, and greenish or yellowish discoloration with an off odor.
- Since chorioamnionitis can adversely affect fetal health, prompt treatment is vital.
- Bacteremia in the mother and pneumonia and meningitis in the fetus are possible complications of chorioamnionitis during pregnancy.
References
- Intrauterine infection (chorioamnionitis).
https://www.tommys.org/pregnancy-information/pregnancy-complications/intrauterine-infection-chorioamnionitis - Chorioamnionitis.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/12309-chorioamnionitis - M.J.Czikk et al; (2011); Chorioamnionitis: from pathogenesis to treatment; Clinical Microbiology and Infection.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1198743X14612088 - Chorioamnionitis.
https://www.stanfordchildrens.org/en/topic/default?id=chorioamnionitis-90-P02441 - Chorioamnionitis.
https://radiopaedia.org/articles/chorioamnionitis?lang=us - Chorioamnionitis.
https://www.birthinjuryhelpcenter.org/birth-injuries/prenatal-problems/chorioamnionitis/ - David A. Smith; Sara M. Nehring; (2025); Bacteremia.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441979/ - Does Chorioamnionitis Recur in Subsequent Pregnancies?
https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2007/0615/p1862.html - Yvonne W. Wu et al; (2003); Chorioamnionitis and Cerebral Palsy in Term and Near-Term Infants.
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/197709 - Endometritis.
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001484.htm
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Miguel Angel Razo Osorio
Read full bio of Dr. Ritika Shah