Image: Shutterstock
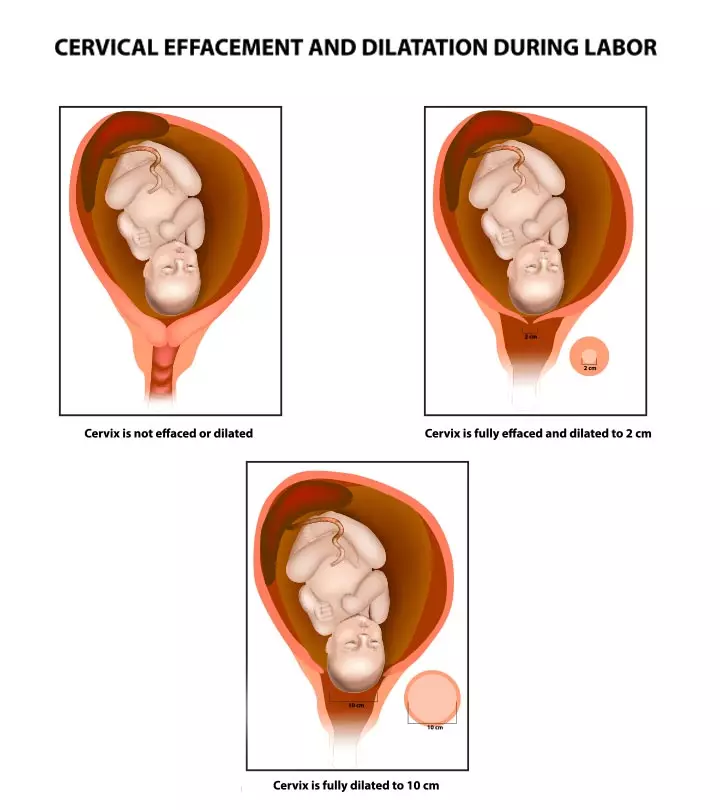
The breech presentation occurs during delivery when the baby’s buttocks, feet, or both emerge first from the birth canal. The birth position may increase the risk of birth defects or congenital malformations. Breech babies’ birth defects may vary from physical issues to genetic disorders.

Babies born breech do not move their heads down towards the birth canal as the due date approaches to be born with vertex presentation. About 3-4% of full-term infants are born with breech presentation (1).
Despite the presence of a breech presentation, not all babies born with it may develop birth defects.
Key Pointers
- The breech position has three types – Frank, incomplete, and complete.
- The breech position may indicate a risk of congenital anomaly, but not all breech babies have them.
- Hip dysplasia, cleft lip or palate, and down syndrome are a few congenital anomalies associated with the breech position.
- Changing the fetal position before the delivery could avert issues linked with a breech birth.
Types Of Breech Babies

There are three types of breech positions (2).
- Frank breech: This is the most common breech position where buttocks are delivered first. Legs are positioned up in front of the body and feet near the head.
- Complete breech: The buttocks are presented near the birth canal. The knees are bent, and the feet are placed near the buttocks.
- Incomplete breech: Baby’s buttocks and a foot are presented in the birth canal. The other leg stays up towards the body like seen in the frank breech. If one foot and buttocks emerge first, it is called footling breech. If both feet appear first since both legs are extended, it is called double footling breech.
Besides these positions, a baby can be in a horizontal position across the uterus. In this position, the shoulder of the baby is positioned such that it will enter the birth canal first. It is called the transverse lie position (3).
 Quick fact
Quick factWhat Causes A Baby To Be Breech?
Some common factors that might be responsible for a baby being in a breech position include (3) (4):
- The mother has been pregnant before.
- The amount of amniotic fluid present is either too much or too little.
- The mother is expecting twins or triplets.
- The uterus has abnormal growths, such as fibroids.
- The uterus has an irregular shape.
- The placenta covers most or a part of the uterus’s opening, a condition known as placenta previa.
- The fetus is preterm.
- The fetus has some type of congenital disability that prevents it from turning in the head-down position.
What Rate Of Breech Babies Have Birth Defects?
There may be a slight increase in the number of birth defects among breech babies. A study noted that 11.7% of infants born breech had at least one congenital anomaly. In comparison, only 5.1% of babies born with vertex presentation had any congenital anomaly (5). This occurred regardless of the term of pregnancy.
The study established that breech presentation at birth may indicate congenital anomalies. Congenital defects could prevent the baby from moving to a cephalic position (head down) before delivery. Although the breech position may indicate a possible congenital anomaly, it may not be noted in all breech babies.
A study showed that the incidence of severe birth injury on breech presentation might differ with the gestational age. The graph below shows that most severe birth injuries due to breech vaginal delivery occurred at 32 weeks gestation. The incidence reduces with a stable occurrence between 37 and 39 weeks. The number of injuries spikes in the 41st week but does not reach a peak like it did at 32 weeks.

Incidence of severe birth injuries in breech delivery at different gestational weeks
Source: Birth injury in breech delivery: a nationwide population-based cohort study in Finland; Archives of Gynecology and ObstetricsWhat Birth Defects Are Associated With Breech Babies?
Studies have shown that the following birth defects are commonly seen in babies born breech (6).
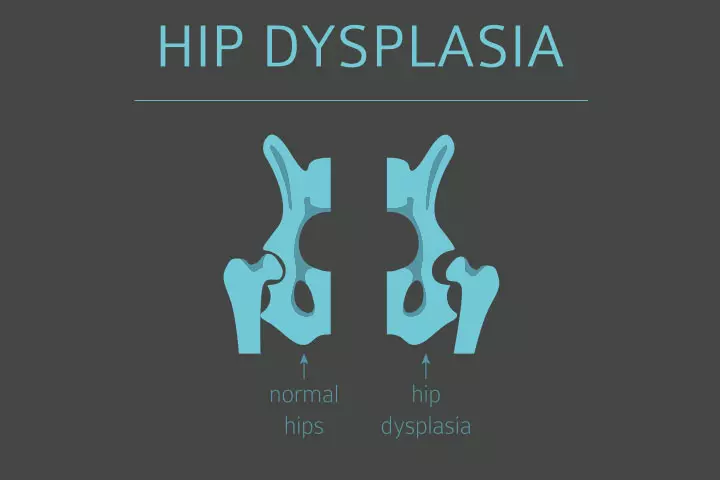
- Congenital hip deformity or hip dysplasia: Breech babies may have congenital hip problems, such as hip dysplasia, since their movements in the womb can be limited. It can be especially common in frank breech where knees are extended. Early detection and treatment of hip dysplasia are crucial for preventing developmental delays in walking and other motor skills.
- Nervous system and musculoskeletal system malformations: Breech babies may have a higher risk of neurological or musculoskeletal disorders due to reduced or lack of movements in the womb. These malformations can be the reason for the reduced ability to turn into the cephalic presentation (vertex) before delivery.
- Structural deformities of fetal ears, face, eyes, and neck: These conditions may affect the fetal rotation to a cephalic presentation near the due date.
- Cleft lip or cleft palate, respiratory and circulatory system problems: These conditions may increase breech presentation due to polyhydramnios (too much amniotic fluid).
- Genital and urinary malformations: These defects may contribute to breech position due to polyhydramnios (too much amniotic fluid) or oligohydramnios (too little amniotic fluid).
- Chromosomal anomalies: Intrauterine growth restrictions associated with chromosomal anomalies may cause breech presentation.

- Down syndrome: Babies with Down syndrome could be born breech due to their inability to turn to vertex position before birth.
Studies have shown that various malformations are associated with breech birth except for digestive system problems. Malformations may primarily cause the baby to fail to rotate to the cephalic presentation before birth.
Complications Of Breech Presentation
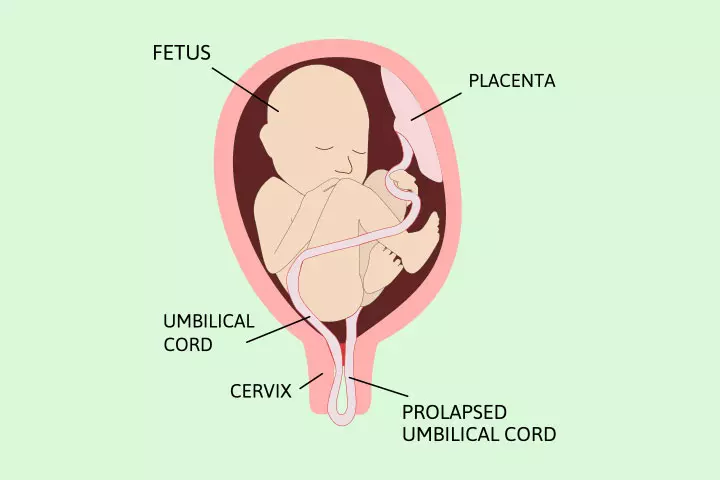
Umbilical cord prolapse and head entrapment are significant problems of breech delivery (7). If the umbilical cord is compressed during breech birth, it could restrict the blood and oxygen flow to the fetus, leading to delivery complications, including premature birth and low birth weight.
Breech birth can be associated with fetal distress in many cases. Delay in delivery and meconium-stained amniotic fluid can be a reason for it. There is also an increased risk of hip dislocation during a breech delivery, which may require neonatal intensive care.
How To Prevent Problems Of Breech Births?
There is no way to prevent birth defects in breech babies. However, problems associated with breech birth could be prevented by changing the position of the fetus before the delivery. The following procedures or techniques may help to avoid breech birth.
1. External cephalic version
It is a procedure that turns the fetus from breech or side-lying (transverse) position to head-down or vertex position before labor. This is usually done at 37 weeks of gestation before the labor begins but rarely done during the labor before the amniotic sac ruptures (3). Research shows that ECV has an average success rate of 60% (15).
Doctors may give tocolytic injections before the procedure to prevent uterine contractions and relax the uterus. After visualizing the baby’s position, placental location, and amniotic fluid volume, the doctor may gently push the abdomen to change the position. The fetus is closely monitored with fetal ultrasound and electronic fetal heart monitoring. If the first attempt fails, the second attempt may be made under epidural anesthesia.
Although complications are rare in the external cephalic version, there is always a possibility. Therefore, the procedure is always done in a hospital where women can have emergency C-sections. It is possible to have a vaginal birth after a successful external cephalic version. If there is no complication after an unsuccessful version, a scheduled cesarean section is done.
ECV may not be tried if there is more than one fetus, known fetal anomalies, abnormalities of the reproductive system, wrong placement of the placenta, or placental abruption (8).
2. Chiropractic care

Women go to a chiropractor during pregnancy mainly to manage pregnancy-related pains and other symptoms. Chiropractic care, however, also involves preparing the woman’s body for labor and childbirth. The Webster technique is a chiropractic method to move the fetus from breech position to normal position. This technique focuses on relaxing the uterus and ligaments, reducing stress on the pelvis. This technique is based on the theory that a more relaxed uterus lets the breech baby turn naturally.
Although it is attempted in chiropractic care, a few existing scientific studies backing the techniques are weak in conclusion (9).
 Quick fact
Quick factFrequently Asked Questions
1. Are breech babies less intelligent?
Some people believe that baby birth positions are related or linked to their intelligence. However, research shows no relationship between a baby’s presentation at birth and their intelligence later in life (10).
2. Do breech babies have learning disabilities?
According to a study, the average frequency of hyperkinesia (state of excessive restlessness and hyperactivity) and learning disability in children born with breech presentation was 14%. On the other hand, it was found to be two percent in children born in vertex position (11). It can be deduced that babies born in the breech position might have learning disabilities. However, it doesn’t happen in all the babies born in this position.
3. Does breech position mean the baby will have Down syndrome?
No clinical studies or research studies were found that could demonstrate that babies born in the breech position will have Down syndrome.
4. Do breech babies have leg problems?
No studies or clinical reports suggest that all babies born in the breech position will have leg problems. Some breech babies after birth may keep their legs in the air for the first few days. However, the legs usually return to their normal position gradually (12).
Congenital disabilities are sometimes caused by fetal malpresentation, such as breech birth. However, it is impossible to generalize that all babies born in breech positions will have congenital disabilities or that babies born with vertex presentation will be healthy. In fact, various maternal and fetal factors, such as the amount of amniotic fluid in the uterus or intrauterine growth restrictions, can cause breech presentations. Therefore, doctors may recommend early hospitalization for interventions or cesarean section delivery if there is a risk of breech presentation or any possible risks for vaginal breech delivery.
Infographic: What Kinds Of Injuries Can Happen During Breech Birth?
Breech birth increases the risk of birth injuries, especially in cases of delayed labor. Birth injuries occur during delivery and may or may not cause permanent damage. In comparison, congenital disabilities are already present from fetal life and are often not curable. Go through the infographic to know common birth injuries during a breech birth.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
Illustration: Common Breech Baby Birth Defects And Their Complications

Image: Dalle E/MomJunction Design Team
In this informative video, you can learn about breech babies, risks, natural vs cesarean birth, and more! Get the facts explained by an experienced midwife.
References
1. Management of Breech Presentation;Royal College of Obstetricians & Gynecologists
2. Breech Presentation;U.S. National Library of Medicine
3. If Your Baby Is Breech;The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
4. Breech Baby;Cleveland Clinic
5. Breech presentation at delivery: a marker for congenital anomaly?;National Library of Medicine
6. Congenital anomalies in breech presentation: A nationwide record linkage study;Wiley Online Library
7. Breech position;Birth Injury Help Center
8. If Your Baby Is Breech;The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
9. Breech repositioning unresponsive to Webster technique: coexistence of oligohydramnios; U.S. National Library of Medicine
10. Martha G Eide et al.; Breech delivery and intelligence: a population-based study of 8,738 breech infants; NCBI (2005)
11. Stefan Fianu &Ingemar Joelsson; Minimal brain dysfunction in children born in breech presentation; Taylor & Francis (1978)
12. Breech baby; University Hospitals Sussex NHS Foundation Trust
13. Breech Births; American Pregnancy Association
14. Caesarean sections; Australian Institute of Health and Welfare
15. External Cephalic Version; U.S. National Library of Medicine
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Supriya Mahajan
Read full bio of Dr Bisny T. Joseph
Read full bio of Rohit Garoo
Read full bio of Vidya Tadapatri