Image: ShutterStock
Gaining some weight during pregnancy is healthy, but for overweight women, excessive weight gain can be concerning. Following diet plans for overweight pregnant women can help you manage your weight while ensuring proper nutrition for both you and your baby. A well-balanced pregnancy diet should include foods from all major food groups while keeping calorie intake in check. An abnormal weight gain during pregnancy invites complications such as preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and even depression. These issues can take a toll on both your and the baby’s health. In this post, we have provided some healthy food choices to include in your pregnancy diet, including tips to make delicious yet balanced meals. Keep reading to learn how to nourish your body and support your baby’s growth safely.
Key Pointers
- A nourishing pregnancy diet for overweight women should include roasted or baked dishes, low-fat dairy, fresh vegetable and fruit salads, whole wheat bread, and lean meats.
- To control weight gain during pregnancy, overweight women should restrict portion sizes, use low-fat cooking oils, minimize sodium intake, and increase fluid intake.
- Overweight women are more likely to have long labor and delivery problems during pregnancy.
- Pregnancy obesity increases the risk of miscarriage, gestational diabetes, and fetal complications.
- Pregnant women should prioritize healthy eating and considerate weight gain.
Why Nutrition Matters During Pregnancy
Consuming nutrient-rich foods during pregnancy is important for the health of both mother and baby. A balanced diet supports fetal development and helps prevent complications. Here are a few reasons why adequate nutrition during pregnancy is important (1) (2) (3):
1. Fetal development
- Adequate nutrition supports critical developmental processes in the growing baby
- Ensures proper brain, organ, and skeletal system formation
- Prevents potential birth defects and developmental challenges
2. Maternal health protection
- Reduces the risks of pregnancy complications like gestational diabetes
- Helps manage weight gain within recommended ranges
- Supports mother’s physical and mental well-being during pregnancy
3. Long-term health implications
- Proper nutrition can influence the child’s future metabolic health
- Reduces the risks of obesity and chronic diseases later in life
Dietary Guidelines For Overweight Pregnant Women

For overweight pregnant women, the focus is on nutrient density rather than simply increasing calorie intake. The goal is to support fetal growth without excessive weight gain. The recommended weight gain during pregnancy varies based on the pre-pregnancy Body Mass Index (BMI) (4).
- BMI 25.0–29.9 (Overweight): The recommended total weight gain during pregnancy is 7.0–11.5 kilograms (approximately 15–25 pounds).
- BMI > 30 (Obese): The recommended total weight gain during pregnancy is 5.0–9.0 kilograms (approximately 11–20 pounds).
So, if you were overweight already, try to keep a close tab on your weight gain during these nine months. Consulting with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian can help in creating a personalized plan that considers individual needs and health status.
 Point to consider
Point to considerDiet Recommendations For Overweight Pregnant Women
If you need to keep an eye on the weighing scale while expecting, you must cut down on your unhealthy calorie consumption. You can remain healthy and disease-free by including nutrient-rich and low-calorie foods in your meal planning. You must maintain your recommended calorie intake and plan your healthy meals during pregnancy accordingly. Registered dietitian Alicia Chacha Miller suggests, “Start with simple, balanced meals that include fiber-rich carbs, lean proteins, and nutrient-dense fats to help support energy, manage hunger, and stabilize blood sugar. Focus on variety and portions. Include satisfying snacks, such as fruit with nut butter or yogurt with seeds, to help meet your growing needs without feeling restricted.”
Foods To Include In A Pregnancy Diet Plan
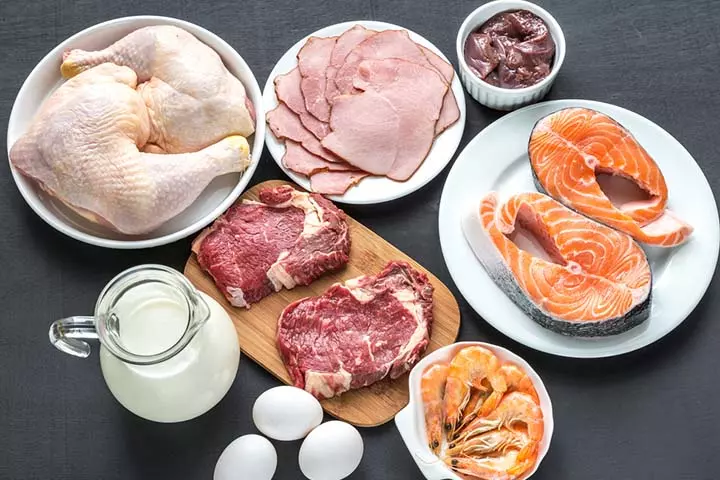

Here are some of the superfoods that your pregnancy-balanced diet plan should include if you are overweight:
- Vegetables: Eating fiber-rich vegetables can keep you full longer, preventing overeating. Some healthy choices include spinach, carrots, sweet potatoes, and tomatoes. It will also help with digestion and prevent constipation (6).
- Fruits: They provide natural sweetness and essential vitamins without adding excessive calories. Fruits such as watermelon, banana, grapefruit, and berries are excellent choices for overweight pregnant women (7).
- Whole grains: Choosing whole grains like brown rice, oatmeal, and whole-wheat bread offers long-lasting energy. They take longer to digest and keep you full longer (8). This keeps you from overeating and helps with healthy weight management.
- Lean proteins: Skinless poultry, fish, beans, and lentils provide protein for fetal growth and muscle maintenance without the extra fat found in processed meats. In addition to protein, lean red meat is a good source of iron, and fish contains omega-3. These nutrients are beneficial during pregnancy (9). Protein also keeps you satisfied, reducing cravings for unhealthy snacks.
- Low-fat dairy: Opting for low-fat yogurt or skim milk ensures you get enough calcium for strong bones without the extra calories from full-fat dairy products (10).
Foods To Avoid Or Limit
While some foods provide essential nutrients, others can contribute to excessive weight gain or pose health risks during pregnancy. Below are some foods to be mindful of during pregnancy (11):
- Foods with added sugar or artificial sweeteners: Foods with added sugars or artificial sweeteners may contribute to unhealthy weight gain and increase the risk of gestational diabetes.
- Sugar-sweetened beverages: Many sweetened drinks, including sodas, fruit drinks, energy drinks, and flavored coffees, are high in calories and sugar with little to no nutritional benefit. A study found that added sugar consumption during pregnancy caused increased gestational weight gain and increased the risk of gestational diabetes, preterm birth, and preeclampsia (12).
- Processed snacks: Processed foods are often formulated to be highly palatable and convenient. Research shows that the consumption of ultra-processed foods (UPF) may lead to excessive gestational weight gain, neonatal adiposity, and potentially other adverse outcomes. The study report states that, “A 1%-point increase in PEI-UPF (percent of energy intake from ultra-processed foods) was associated with a 1.33 kg increase in gestational weight gain (13).”
- Refined carbohydrates: Studies have shown that diets high in high-glycemic index carbohydrates, including processed grains, can contribute not only to greater weight gain in the mother but also potentially to larger babies (14). Examples include flour, bread, baked goods, confectioneries, and cereals.
- Fried and fast foods: The fats contained in such foods are calorie-dense and can readily contribute to excessive weight gain during pregnancy. Research also suggests that maternal consumption of unhealthy fats can have long-term consequences for the child’s health, potentially influencing their metabolism and increasing the risk of childhood obesity and metabolic defects (15).
While weight loss is not recommended during pregnancy, making mindful food choices can help manage weight gain and reduce the risk of complications. In addition to choosing the right foods, following some dietary strategies can ensure optimal nutrition.
Safe Weight Management During Pregnancy
A US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report shared that pre-pregnancy obesity increased from 26.1% in 2016 to 29.0% in 2019 (16). Since being overweight/obese before pregnancy can raise your chances of gaining more than the recommended weight when pregnant, it is imperative to maintain weight.
Here are a few simple tips that can help you regulate your weight gain during pregnancy:
- As it would be difficult to change your eating habits drastically, you can portion control and limit the portion size of the foods you consume.
- Eating six smaller meals throughout the day can also be a helpful strategy for managing hunger and preventing indigestion.
- Use olive oil or low-fat butter instead of normal cooking oil. Excess fat intake or consumption can adversely affect your health and the growth of the fetus.
- Reduce your sodium intake by using low-fat unsalted butter and less salt while cooking.
- If craving something sweet, consider adding dried fruit or fruit puree to dishes to sweeten them naturally.
- Increase the intake of water, fruit juices, and other unsweetened beverages to keep your body hydrated.
- If you are used to having sugar in hot drinks, gradually reduce the amount until you can eliminate it altogether.
- Choose roasted or baked foods instead of unhealthy fried ones.
- Homemade foods and healthy snacks are far better than high-calorie junk or processed foods.
- Engaging in regular, pregnancy-safe exercises can also help manage weight gain. Consult with your healthcare provider and start an exercise regimen y to ensure it is safe for your individual condition.
If you have concerns about your weight or feel you need support in developing a healthy eating plan, speak with your doctor, midwife, or a registered dietitian for personalized advice. It is strongly advised against following self-devised diets during pregnancy.
Risks Of Being Overweight During Pregnancy
Obesity during pregnancy can lead to complications like hypertension, diabetes, preeclampsia, fetal macrosomiai A condition where a baby is born with a weight that is significantly higher than the average (usually 4000 or 4500 g) ,increased cesarean delivery rates, higher incidence of wound infections, etc. Some of the other health issues overweight women are likely to face during pregnancy include the following: (17)
- Miscarriage: Due to the elevated level of BMI, you are at greater risk of miscarriage than other pregnant women.
- Gestational diabetes: If your BMI is above 30, you are more prone to develop gestational diabetes in comparison to other would-be moms.

- Delivery complications: Being obese, you are also prone to preterm labor. An unhealthy weight during pregnancy also increases the chance of needing birth intervention, including induced labor, cesarean and shoulder dystociaiA condition where the baby’s shoulders become stuck during the birthing process .
Your obesity can cause the following birth defects in your baby:
- Neural tube defects, such as spina bifidaiA congenital disorder where the spinal cord doesn't fully develop, leading to physical and neurological complications
- Heart defects
- Cleft palateiA congenital disability where the baby’s palate (roof of the mouth) is abnormally developed
- Limb reduction defects (20)
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I get in shape while pregnant?
Exercising is beneficial during pregnancy as it can strengthen your muscles and improve circulation. Safe and medically approved exercises may help your body adapt better to the changes, prepare you for the delivery, and help you get back in shape after the delivery (21).
2. Can I go on a diet to lose weight while pregnant?
Pregnancy is not the time to go on a diet. The fetus is dependent on the mother for nutrition, and weight-loss diets could hinder the baby’s growth and development. If you are overweight or obese, your medical advisor and dietitian will prescribe a suitable diet.
3. Are there any risks associated with following a diet plan during pregnancy?
There is no risk associated with following a diet plan during pregnancy. Rather, following a healthy diet plan is vital for you and your unborn baby’s health. Talk to your healthcare provider or a certified nutritionist to prepare an individualized diet plan. Remember, a diet chart for pregnant women can be incredibly beneficial, provided you follow it with care under expert guidance.
4. What types of exercises can overweight pregnant women do in addition to following a diet plan?
Some exercises that are safe during pregnancy include walking, cycling, swimming, pilates, yoga, and jogging (22).
5. How can overweight pregnant women overcome cravings and the desire to eat unhealthy foods?
Unhealthy food cravings can be swapped with healthy foods. To overcome sugar cravings, try eating whole fruits or freshly squeezed fruit juice, and include healthy snacks like roasted chickpeas, sweet potato, fresh salads, smoothies, and roasted meats and vegetables instead of junk fried foods.
6. Can overweight pregnant women still eat out or order takeout while following a diet plan?
Yes, an overweight pregnant woman can still eat out, provided the food is eaten in moderation, from a reliable restaurant, and not very often.
7. What is a sample meal plan for overweight pregnant women?
Focus on keeping your diet balanced while controlling calories. Include foods like quinoa, brown bread, and seasonal fruits for breakfast. For lunch, try brown rice with grilled chicken salad and greens, or a chickpea salad with mixed greens, cherry tomatoes, cucumber, and a light olive oil dressing. An apple with a small handful of nuts, like almonds, is a great afternoon or evening snack. For dinner, have baked salmon with steamed broccoli, vegetable stir-fry, healthy lentil soup, or yogurt.
8. What are the key nutritional requirements for overweight pregnant women?
Overweight pregnant women need the same essential nutrients as all pregnant women, with some specific considerations. They require adequate protein (about 75-100 g daily), iron (27mg), folate (600 mcg), calcium (1000 mg), omega-3 fatty acids, and a few important vitamins (23) (24). However, their caloric needs may be slightly lower than normal-weight pregnant women.
9. Is it safe to follow a low-carb or keto diet while pregnant and overweight?
Healthcare professionals generally recommend that pregnant women focus on eating a balanced diet with appropriate portions rather than following restrictive eating patterns. It is essential to consult a doctor or a registered dietitian before following any diet during pregnancy, especially restrictive ones like low-carb or keto, to ensure that both maternal and fetal health are not compromised.
10. What role does hydration play in managing weight during pregnancy?
Proper hydration supports digestion and helps prevent overeating by promoting a sense of fullness, which can be beneficial in controlling calorie intake (25). The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends that pregnant women consume 8 to 12 cups (64 to 96 ounces) of water daily to support bodily functions and fetal development (26).
Pregnancy-induced food cravings and the wrong assumption that you need to eat for two may cause excess weight gain, especially if you are overweight at the time of conception. Gaining excess weight increases the risks of pregnancy complications and may also be detrimental to the fetus. However, diet plans for overweight pregnant women should focus on cutting down unhealthy calories without compromising the nutritional requirements. Whole fruits, whole grains, salads, and lean meat are some of the most nutritious foods to eat during pregnancy. Eating these foods in moderation as a part of a well-balanced diet may help prevent excess weight gain during pregnancy.
Infographic: Dietary Tips For Overweight Pregnant Women
Pregnancy is a time of physical and hormonal changes, and being overweight can complicate matters. However, implementing the right dietary strategies is the key to managing excess pregnancy weight gain. Our infographic could be a handy guide for pregnant women who are overweight, so skim through it and switch to healthier food choices to have a healthy pregnancy and baby. Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Illustration: Diet Plans For Overweight Pregnant Women - Everything You Need To Know

Image: Stable Diffusion/MomJunction Design Team
References
- Nicole E Marshall et.al; (2025); The importance of nutrition in pregnancy and lactation: lifelong consequences.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9182711/#:~:text=The%20message%20should%20be%20%E2%80%9Ceat - Wang Fleischhacker; (2025); The importance of diet during pregnancy: Impacts on the developing baby and maternal health.
https://www.revistanutricion.org/articles/the-importance-of-diet-during-pregnancy-impacts-on-the-developing-baby-and-maternal-healt-105951.html - Healthy eating in pregnancy.
https://www.nidirect.gov.uk/articles/healthy-eating-pregnancy#:~:text=During%20pregnancy%2C%20it’s%20important%20to - Pregnancy and diet.
https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/healthyliving/pregnancy-and-diet - Weight Gain During Pregnancy.
https://www.cdc.gov/maternal-infant-health/pregnancy-weight/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth/maternalinfanthealth/pregnancy-weight-gain.htm - Have a healthy diet in pregnancy.
https://www.nhs.uk/pregnancy/keeping-well/have-a-healthy-diet/ - 7 Fruits That Can Help You Lose (or Maintain Your) Weight.
https://www.keckmedicine.org/blog/7-fruits-that-can-help-you-lose-or-maintain-your-weight/ - Cereals and wholegrain foods.
https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/healthyliving/cereals-and-wholegrain-foods#wholegrains-and-weight-management - Pregnancy: healthy weight and weight gain.
https://raisingchildren.net.au/pregnancy/health-wellbeing/healthy-lifestyle/healthy-pregnancy-weight-and-weight-gain - Low-fat or Fat-free Dairy.
https://www.health.ny.gov/prevention/nutrition/wic/healthy_lifestyles/dairy.htm#:~:text=Dairy%20products%20are%20an%20important - Managing your weight gain during pregnancy.
http://mountsinai.org/health-library/selfcare-instructions/managing-your-weight-gain-during-pregnancy - M. I. Goran et.al; (2018); Effects of consuming sugars and alternative sweeteners during pregnancy on maternal and child health: evidence for a secondhand sugar effect.
https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/proceedings-of-the-nutrition-society/article/effects-of-consuming-sugars-and-alternative-sweeteners-during-pregnancy-on-maternal-and-child-health-evidence-for-a-secondhand-sugar-effect/2F31AE3E8099B7989ABB69F4E1EB97F5 - Karthik W. Rohatgi et.al; (2017); Relationships between consumption of ultra-processed foods, gestational weight gain and neonatal outcomes in a sample of US pregnant women.
https://peerj.com/articles/4091/ - James F. Clapp III; (2002); Maternal carbohydrate intake and pregnancy outcome.
https://www.cambridge.org/core/services/aop-cambridge-core/content/view/28F8E1C5E1460E67F2F1CE0C1D06EE81/S0029665102000095a.pdf/div-class-title-maternal-carbohydrate-intake-and-pregnancy-outcome-div.pdf - What NOT to Eat During Pregnancy: Foods You Should Avoid While Pregnant and Why.
https://www.fhcsd.org/prenatal-care/what-not-to-eat-during-pregnancy-foods-to-avoid/ - Increases in Prepregnancy Obesity: United States, 2016–2019.
https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db392.htm - Overweight/Obesity and Pregnancy.
https://health.hawaii.gov/mchb/files/2013/05/obesity.pdf - Being overweight in pregnancy and after birth.
https://www.rcog.org.uk/for-the-public/browse-our-patient-information/being-overweight-in-pregnancy-and-after-birth/ - Overweight and pregnant.
https://www.tommys.org/pregnancy-information/im-pregnant/weight-management/overweight-and-pregnant - Adolfo Correa and Jessica Marcinkevage; (2013); Prepregnancy obesity and the risk of birth defects: an update.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5866281/ - Exercise in pregnancy.
https://www.nhs.uk/pregnancy/keeping-well/exercise/ - Pregnancy and exercise.
https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/healthyliving/pregnancy-and-exercise#suggested-exercise-activities-during-pregnancy - Pregnancy Nutrition
https://americanpregnancy.org/healthy-pregnancy/pregnancy-health-wellness/pregnancy-nutrition/ - Nutrition During Pregnancy.
https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/nutrition-during-pregnancy - Amanda Burls et.al; (2019); Drinking extra water or other non‐caloric beverages for promoting weight loss or preventing weight gain.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6426280/ - How much water should I drink during pregnancy?
https://www.acog.org/womens-health/experts-and-stories/ask-acog/how-much-water-should-i-drink-during-pregnancy
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Mona Hardas
- Alicia Chacha Miller is a registered dietitian specializing in maternal and pediatric nutrition. She holds an MS in Nutrition Science from the University of Southern California and founded Cardamom Nutrition.
 Alicia Chacha Miller is a registered dietitian specializing in maternal and pediatric nutrition. She holds an MS in Nutrition Science from the University of Southern California and founded Cardamom Nutrition.
Alicia Chacha Miller is a registered dietitian specializing in maternal and pediatric nutrition. She holds an MS in Nutrition Science from the University of Southern California and founded Cardamom Nutrition.
Read full bio of Ria Saha
Read full bio of Swati Patwal
Read full bio of Lorraine Teron

 Quick fact
Quick fact