Image: Shutterstock
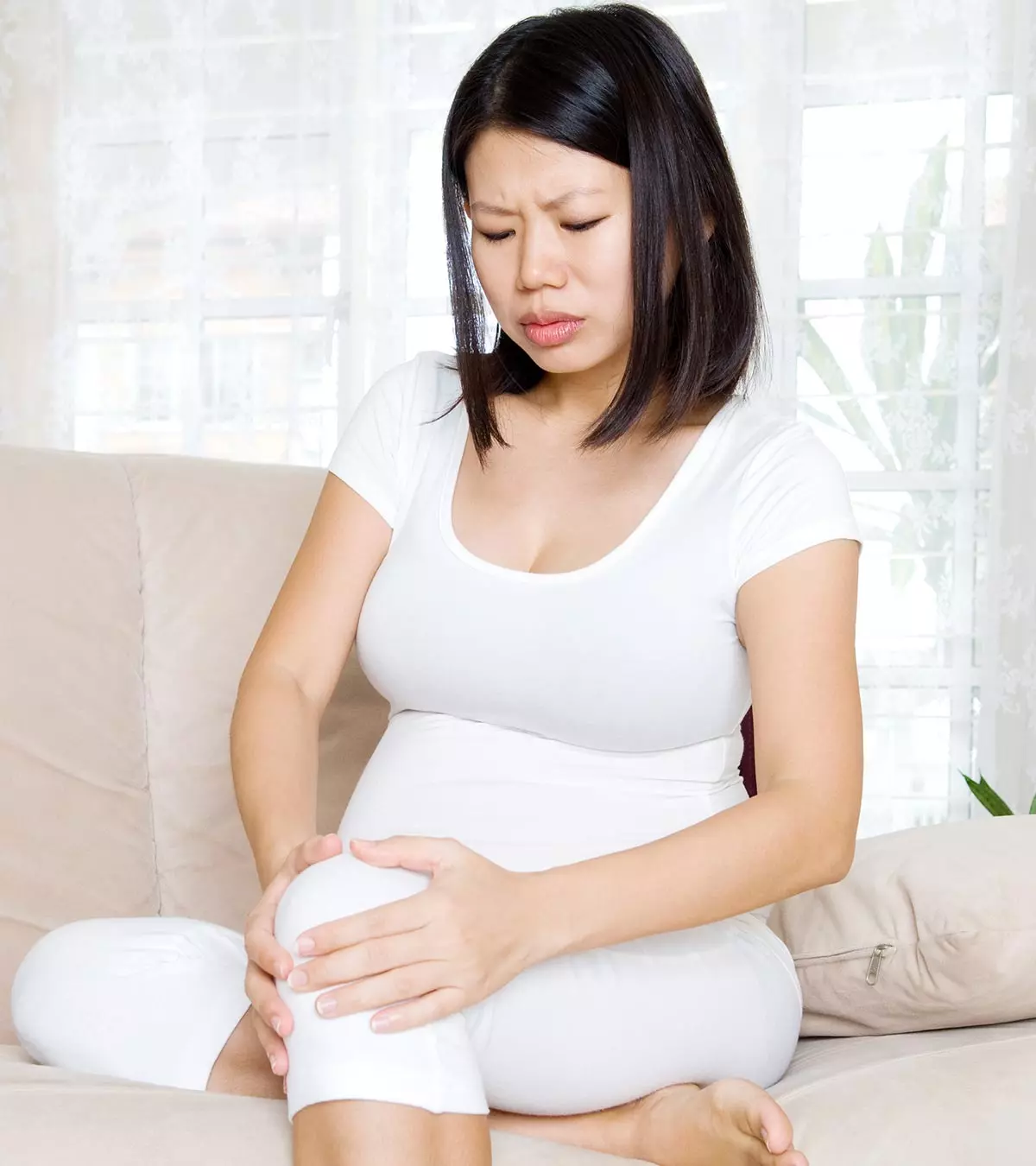
Pregnant women often experience body aches and pains. As pregnancy progresses, your body weight increases and the bone joints become softer in preparation for childbirth at later stages. All these factors may contribute to knee pain in pregnancy. In addition, your growing baby bump exerts pressure on the pelvic floor muscles, uterus, and joints and ligaments, especially of the lower extremities. Read this post as we explain the various causes and complications of knee pain in pregnant women and give you a few tips on managing it.

Key Pointers
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy cause joints to become softer.
- Weight gain during pregnancy can lead to knee pain.
- Knee pain can also be caused by excessive exercise, falls, and standing or walking for extended periods.
- Low-impact exercises for short periods can help alleviate knee pain.
- Resting feet regularly, wearing comfortable shoes, using hot or cold compresses, and managing weight gain can also help relieve knee pain.
- In case of severe pain, it is recommended to consult a doctor for prompt treatment or medication.
What Are The Causes Of Knee Pain During Pregnancy?
Knee pain occurs in most women, but there are different reasons for knee pain during pregnancy.
- Hormonal changes: In your third trimester, the secretion of relaxiniA hormone produced by the ovaries that help relax the muscles and joints during pregnancy and prepare the body for childbirth hormone loosens up the pelvic ligaments and tendons to prepare for childbirth. They will not only affect the ligaments of the pelvic region but also loosen the ligaments and tendons of the knees (1).
- Weight gain: The gradual increase in weight during pregnancy will exert strain on the knees, leading to knee pain. This is intense if it is your first pregnancy, as the body may not be able to bear the extra weight (2).

- Exercises: Too much exercise during pregnancy could also weaken the knees. Squats during pregnancy may especially lead to knee pain (3).
- Falls and injuries: Sudden falls, strain, or knee injuries as a result of the changing body will also result in knee pain (4).
- Walking or standing: Knee pain will also develop due to the extended periods of walking or standing when the knees are forced to carry excess weight for longer (5).
- Deficiency of calcium: The need for calcium increases during pregnancy (6), and might result in a deficiency if the body does not take the right amounts. It, therefore, raises the risk of knee pains.
 Quick fact
Quick factAre There Any Complications Associated With Pregnancy Knee Pain?
If knee pain is not treated on time, it might lead to certain complications in the future.
- Osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease, will develop in the later stages. According to data from the National Institutes of Health, it has been found that around 3.3 to 3.6% of the world’s population is affected by osteoarthritis (15). As a consequence, you may experience joint stiffness, pain, and locking of knee joints (7). Interestingly, a small study showed improvements in inflammatory arthritic pain in pregnant women with existing arthritis. However, this remission has been observed to be short-lived, and the condition usually recurs after delivery (16).
- Damage in the protective cartilage and ligament around the knee joints could lead to difficulties in walking, running, and bending in the future (8).
Managing knee pain becomes essential to make pregnancy a comfortable time for the mom-to-be.
When To See A Doctor
It is advisable to seek immediate medical attention if the pregnant women has experienced (14) (17):
- A fall or a sprain
- Worsening knee pain over time
- Knee pain is accompanied by numbness or tingling
- Increased stiffness in knees
- Knee pain with sudden swelling or water weight gain in legs
- If the pain is affecting their mobility, like climbing stairs and walking
How To Manage Knee Pain During Pregnancy?
Here are a few ways in which you can try to alleviate knee pain during pregnancy (9) (14):
- Exercise: Being active during pregnancy is important for maintaining a healthy weight and easing knee pain. Low-impact exercises such as moderate walking, yoga, and swimming will strengthen your quadriceps and offer support to your knees. They might, therefore, prevent knee pain.
- Give some rest to your feet: Do not strain your feet too much and rest more as you start to gain weight while pregnant. It will help ease your knee pain.
- Get the right shoes: Use shoes that are well-cushioned for proper arch support. The cushions act as shock absorbers and prevent knee pain during early pregnancy. It may be a better choice to avoid wearing heels during pregnancy.
- Manage your body weight: Try maintaining your weight as gaining weight too quickly is bad for the joints. On average, you can put around 15 to 25 pounds throughout pregnancy.
- Use knee braces: Wear a knee brace that comes with a doughnut hole in the center when you are walking or indulging in other physical activities. They offer support to the loose ligaments and tendons around the knee and help to control the pain.

- Hot and cold compress: Take a hot water bath or apply a heating pad to the knees, followed by an ice pack. This alternative physical therapy will reduce the pain, inflammation, and swelling around the knee joints.
- Massage therapy: Getting massage therapy will help in relieving joint pains and stiffness. They also help in improving the range of motion.
- Improve your diet: Include a balanced diet of all essential nutrients. Increase the intake of omega-3 fatty acids, calcium, and vitamin D to relieve joint pains and stiffness.
- Rest well: Take enough rest as it helps ease joint or knee pains.
If you have severe knee pain, swelling, or pain that doesn’t improve with self-care, it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider. Addressing the issue early can help prevent complications.
 Quick fact
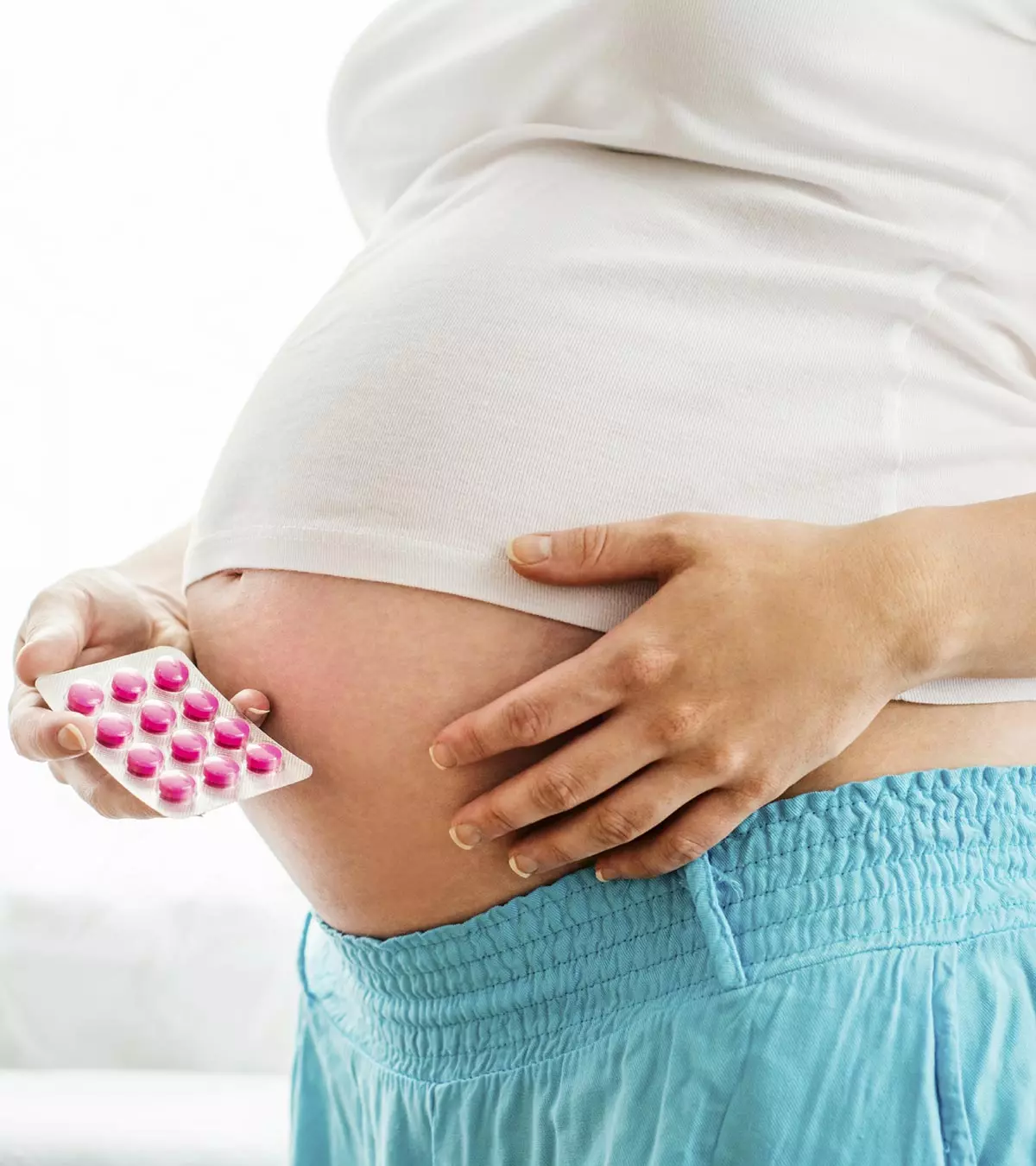
Quick factTreatment For Joint Pain During Pregnancy

The safest over-the-counter medicine your doctor would prescribe is acetaminophen (paracetamol) which helps relieve mild joint pain. Take only small dosages, or as prescribed by the gynecologist, since excessive use is associated with liver damage (10) ( (11). A physical therapy called soft tissue mobilizationiA manual therapy that involves hands-on techniques by licensed physical therapists to address soft tissue restrictions, such as muscles, ligaments, and fascia, to improve mobility and reduce pain (STM) is also helpful in preventing and managing knee pain in pregnant women during their first trimester. However, it is especially recommended for pregnant athletes (17).
Avoid soothing creams and ointments that contain methyl salicylate as they can cause a burning sensation on the skin (12).
Can You Prevent Knee Pain During Pregnancy?
You can’t prevent knee pain unless it is due to a fall or injury. Try and maintain your weight as increased body weight leads to sore knees and causes knee pain. Give enough rest to your body to avoid joint pains and include foods rich in calcium and omega-3 fatty acids after consulting your orthopedist.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do I rest in the proper position during knee pain?
Use pillows to support your legs. If you sleep on your back, place a pillow beneath your legs. Similarly, place a pillow between your calves if you prefer to sleep sideways. If you have knee pain, you can bend your knees, but try not to sleep with your legs crossed (18).
2. Why do my knees hurt at night during pregnancy?
The growing fetus might apply pressure on the blood vessels and nerves based on the position. This stress on the legs while lying on the back could result in increased knee pain at night.
3. Can knee pain during pregnancy affect my delivery?
Knee pain during pregnancy usually doesn’t directly affect delivery, but if the pain is severe, it could limit your movement and make labor more difficult. It’s important to share any concerns with your healthcare provider.
Knee pain is one common pregnancy-related physical discomfort that can be caused due to various factors. Knee pain can impair your pregnancy if it is severe. Therefore, controlling it is critical for a safe and successful pregnancy. Although knee pain while pregnant is unavoidable, there are certain things you can do to reduce the pain, such as low-impact pregnancy exercises, getting enough rest, wearing the proper shoes, and being the right weight. Following these basic steps can help you prevent any postpartum complications, but if your condition does not improve, visit your doctor.
Infographic: How To Manage Knee Pain During Pregnancy?
Expectant mothers often experience knee pain due to the added weight and pressure on their joints as the baby grows. Refer to the infographic below for suggestions on dealing with this problem. However, if the pain persists or becomes severe, it is advised to consult a doctor for further evaluation and treatment.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
Illustration: Knee Pain During Pregnancy: Causes And Ways To Manage It

Image: Dall·E/MomJunction Design Team
Find answers to your concerns about experiencing knee pain during pregnancy and expert tips on how to manage it in this video.
References
1. Hyunju Yoo et al.; Changes in the spinal curvature, degree of pain, balance ability, and gait ability according to pregnancy period in pregnant and nonpregnant women; J Phys Ther Sci (2015)
2. Spahn G et al.; [Knee-related Pain Problems during Pregnancy Correlate with an Increase in Body Weight. Results of a Prospective Study].; Z Geburtshilfe Neonatol (2015)
3. Exercises During Pregnancy: 8 Exercises and Stretches You Can Do at Home; American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
4. Knee Sprains and Strains; University Health Sciences (2011)
5. Hiroki Sugiura & Shinichi Demura; Effects of Mild and Severe Knee Joint Pain on Various Activities of Daily Living in the Female Elderly; Pain Res Treat (2013)
6. Pregnancy, Breastfeeding and Bone Health; NIH Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases ~ National Resource Center (2015)
7. Osteoarthritis of the knee; Orthopedics University of Colorado (2019)
8. Knee Pain and Problems; Columbia University Department of Rehabilitation and Regenerative Medicine
9. Knee Pain; Cedars-Sinai
10. A P Dwivedi and D Erkan; Top 10 Series: Lupus and Pregnancy; Hospital for Special Surgery (2010)
11. Overdoing acetaminophen; Harvard Health (2009)
12. The Burning Issue with Pain Relief Creams; Medsafe – New Zealand Medicines and Medical Devices Safety Authority
13. ONE-QUARTER OF WOMEN IN AN OBSTETRIC POPULATION REPORT SEVERE KNEE DYSFUNCTION; Massachusetts General Hospital
14. Treating Joint Pain Naturally During Pregnancy; American Pregnancy Association
15. Rouhin Sen and John A. Hurley; Osteoarthritis; StatPearls; NIH (2025)
16. Why pregnancy pauses the pain of arthritis; Fred Hutch Cancer Center
17. Treating Anterior Knee Pain in Pregnant Athletes; Massachusetts General Hospital
18. Pregnancy and Posture; Johns Hopkins Medicine
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Kajari Mukherjee
Read full bio of Rebecca Malachi
Read full bio of Swati Patwal
Read full bio of Aneesha Amonz