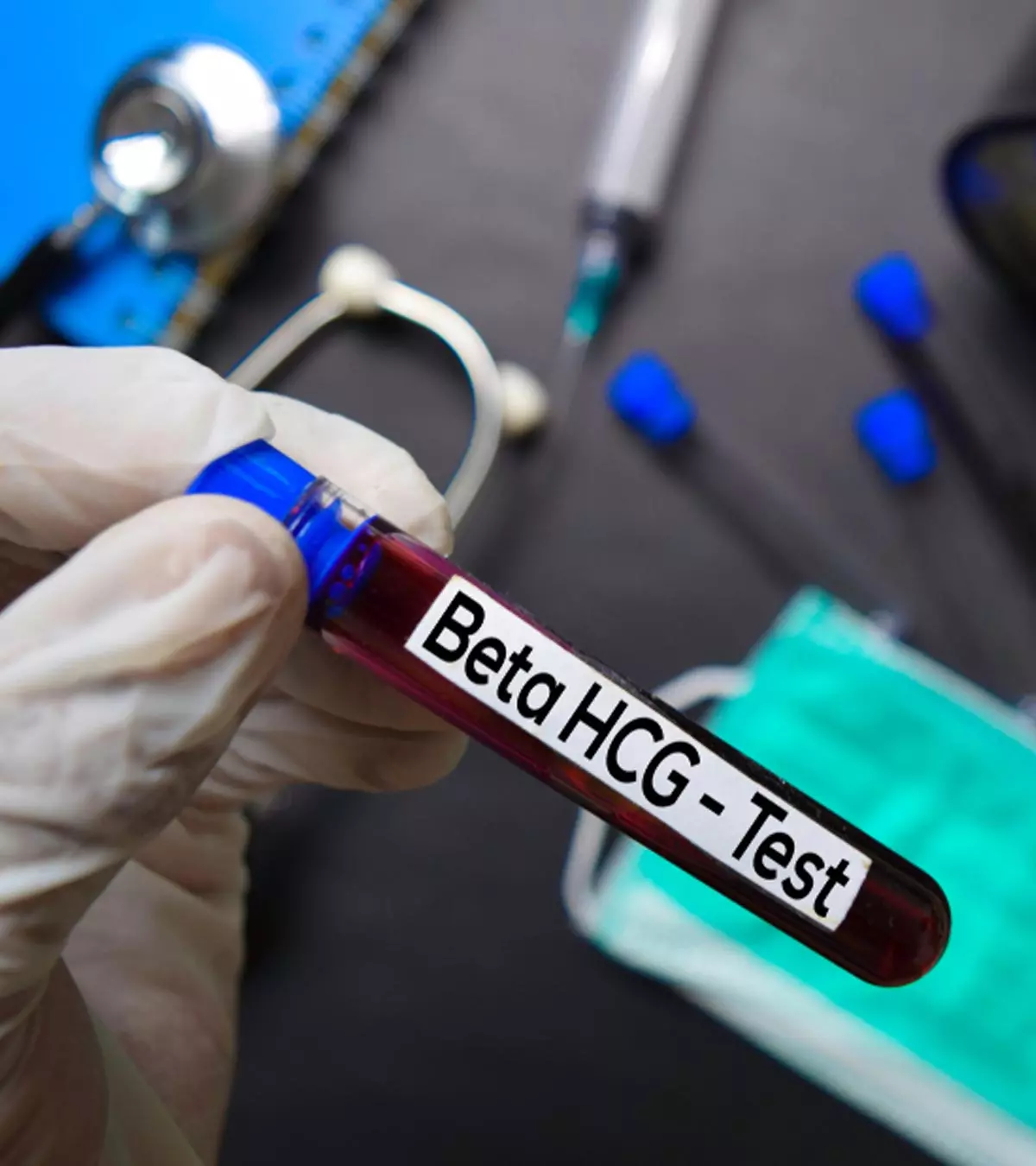
Image: Shutterstock
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone primarily produced by the placenta, is tested in the blood and urine to detect pregnancy. The hCG blood test in pregnancy can detect pregnancy up to a week before your period. This is because hCG levels can be detected in blood as early as six days of embryo implantationiProcess by which the embryo (after fertilization) attaches to the uterine wall. .

Peak hCG levels are attained in the first 14 to 16 weeks after your last menstrual period. After that, they start declining and become stable for the rest of the pregnancy (1).
Read this post to know about the hCG blood test, when to go for it, how to detect the results, and the test’s accuracy.
Key Pointers
- An hCG pregnancy blood test can be carried out six to eight days post-implantation and is of two types, namely qualitative and quantitative.
- A qualitative test gives a positive or negative result, whereas a quantitative test gives numeric results indicating the hCG levels in the blood.
- Certain factors such as ongoing medications, underlying health issues, or recent pregnancy loss may alter the results.
What Is hCG Blood Test?

hCG blood tests detect the presence of the hCG hormone in the bloodstream, which can help in assured pregnancy confirmation. You can undergo these tests only at a clinic.
The two types of hCG blood pregnancy tests that you might have to take include:
- Qualitative hCG test: It checks for the presence of hCG in your blood and gives either a positive or negative result (2).
- Quantitative hCG test: It measures the amount of hCG in your blood. It might help determine the exact age of the fetus or detect pregnancy complications, such as miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy—a complication in which the embryo implants outside the uterus (3). It also helps to monitor patients with molar pregnancies and GTD.
A quantitative hCG blood test is also referred to by other names, including:
- Beta hCG blood test
- Repeat quantitative beta-hCG test
- Quantitative serial beta-hCG test
- Quantitative blood pregnancy test
How Soon Can A Quantitative hCG Test Detect Pregnancy?

An early pregnancy can be detected through an hCG blood test as soon as six to eight days after implantation of embryo (4). This means that it can detect pregnancy ten days to a week before your expected period date (5).
How Accurate is The hCG Blood Test For Pregnancy?
Blood tests are about 99% accurate. However, they may give false-positive or false-negative results in rare cases. A small sample of blood is enough to detect the presence and extent of hCG hormone levels. Also, hCG blood test is more reliable than hCG urine pregnancy test as it can detect even low levels of hCG and thus detect pregnancy much earlier (6).
The factors that could affect the hCG blood test results could be (7):
- Medications, especially fertility drugs and injections
- Presence of certain tumors (such as germ cell tumors), molar pregancy and GTD
- Multiple pregnancies like twins or triplets
- Recent pregnancy loss
- Timing of the test
- Individual health conditions
Why Do You Need An hCG Blood Test?

An hCG blood test is usually done for the following reasons (2) (3) (7):
- To determine pregnancy
- To know the fetal age
- To diagnose abnormal pregnancies such as molar pregnancy and ectopic pregnancy
- To detect a possible miscarriage
- As part of a screening test for Down syndrome
- To diagnose abnormal conditions (such as ovarian tumors) in non-pregnancy cases
What Are The Other Reasons For Performing Beta hCG Blood Test?
hCG is considered a tumor marker as it is present in some types of cancers.
The conditions in which the hCG hormone is likely to be present include (9) (10).
- Cancers of the ovaries and uterus
- Trophoblastic tumoriRare tumors that typically develop in the placental tissues in the early weeks of pregnancy.
- Hydatidiform mole
- Testicular cancer (in the case of men)
hCG levels are found to be elevated in the case of cancers of the lungs, liver, stomach, and pancreas too.
How Is The b-hCG Test Performed?
The test is similar to any typical blood test. It requires a small amount of blood drawn from the vein in the arm (called venipuncture) and requires no special preparation. However, you should inform your doctor if you are taking any drugs, herbal preparations, nutritional supplements, or homeopathiciAn alternative treatment intervention where medications are usually obtained from natural sources. medicines as they might affect the results.
The test involves the following steps (8):
- The phlebotomist (a technician who collects blood samples) wraps an elastic band around the upper arm. This causes the veins to swell so that they are visible.
- The site (the area where the vein is visible and its surrounding region) is then cleaned with an antiseptic.
- A needle is gently inserted into the vein and the blood sample is collected in a vial.
- The elastic band and the needle are removed.
- The site is covered using a cotton gauze or an adhesive bandage to stop any excessive bleeding.
- The blood sample is sent to the laboratory for analysis.
Meltem, a mother and teacher, shares her experience with the test during pregnancy. She recounts, “I went to the hospital with my hubby, and I took a blood test. After a few hours, they sent me the result on the internet. My Beta HCG was 4884 mIU/mL. It means pregnancy is positive, and it is a high and very good Beta HCG level. When I learned that I was pregnant, I was pregnant for 4 weeks and 4 days (i).”
Does hCG Blood Test Pose Any Risks?
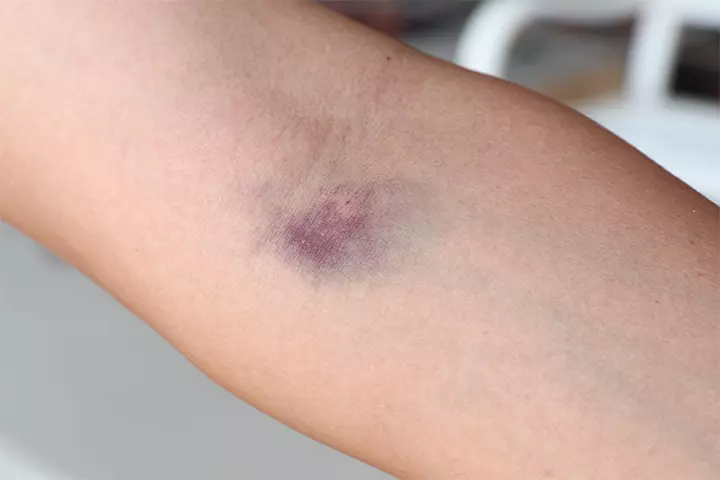
There may not be any major risks of an hCG test. The effects might be momentary. Some of them are (7) (11):
- Pain or a stinging sensation at the puncture site
- Lightheadedness
- Bleeding under the skin (hematoma)
- Infection if the skin is broken
How To Read hCG Blood Test Results?
In a qualitative beta hCG test,
- A positive result indicates that you are or were recently pregnant.
- A negative result indicates that you are not pregnant or the test is taken too early (2).
In a quantitative beta hCG test,

The result is given as a number (in milli-international units per milliliter – mIU/mL) that indicates the concentration of hCG hormone in the blood. The levels rise rapidly during the first trimester, and then decline and become steady over the rest of the pregnancy. The levels may vary depending on your gestational age. Your doctor can explain what the specific levels mean in your pregnancy.
In a non-pregnant woman, the levels would be less than 3mIU/mL (12).
| Weeks after the last menstrual period (LMP) | Normal hCG range (mIU/mL) |
|---|---|
| 3 | 5 – 72 |
| 4 | 10 – 708 |
| 5 | 217 – 8,245 |
| 6 | 152 – 32,177 |
| 7 | 4,059 – 153,767 |
| 8 | 31,366 – 149,094 |
| 9 | 59,109 – 135,901 |
| 10 | 44,186 – 170,409 |
| 12 | 27,107 – 201,165 |
| 14 | 24,302 – 93,646 |
| 15 | 12,540 – 69,747 |
| 16 | 8,904 – 55,332 |
| 17 | 8,240 – 51,793 |
| 18 | 9,649 – 55,271 |
Your healthcare provider will help you in interpreting the result.
A higher hCG level than the normal range may mean any of the following (3):
- Multiple pregnancies (such as twins or triplets)
- Uterine choriocarcinomasiA rare, aggressive tumor developing in the uterine tissues in women.
- Hydatidiform mole or molar pregnancy
- Ovarian cancer
A lower hCG level than the normal range may mean any of the following (3):
- Incomplete miscarriageiA condition where some fetal tissues remain in the uterus following a miscarriage (loss of pregnancy).
- Fetal death
- Ectopic pregnancy
 Quick tip
Quick tiphCG Blood Test Results: False Positives And False Negatives
It may be possible to get false results from an hCG test similar to a urine pregnancy test at home.
- False-positive pregnancy test result: The test shows positive even though you are not pregnant. You may get a false-positive result if you are on any medications or injections (containing hCG) such as those used in fertility treatments or have certain cancers (7).
- False-negative pregnancy test result: In this case, the test result shows negative, but you are pregnant. It may happen if the test is taken too early, before there is enough hCG produced in the blood. Medications or harmful habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol may also give a false-negative test result (13).
 Do remember
Do rememberIf the test shows negative, and if you think you are pregnant, the doctor might recommend the test again in a few days.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How much hCG is needed for a positive blood pregnancy test?
A quantitative maternal serum screening can detect beta hCG at levels as low as 1 to 2 mIU/mL (14). Your doctor might recommend re-testing if you have a high-risk pregnancy because hCG doubles every two to three days early on in a viable pregnancy.
2. What are hCG levels for twins?
The amount of hCG in one’s blood can give information about the pregnancy and the baby’s health. hCG levels can vary widely among different women with normal pregnancies (14), and there is no set number. However, unusual numbers or higher than normal ranges may indicate a twin pregnancy (15). Nevertheless, a twin pregnancy cannot be confirmed by a blood test, and only an ultrasound can confirm a twin pregnancy (16).
3. Should I check my hCG level regularly?
Doctors do not check hCG levels regularly unless you show worrisome signs during pregnancy, such as bleeding, severe cramping, or a history of miscarriages (17).
Although the hCG urine test is widely used in home-based pregnancy test kits, the hCG blood pregnancy test can identify pregnancy even before a urine test. They are of two types, including qualitative hCG test to check the presence of hCG in blood and quantitative hCG testing to assess fetal age or any pregnancy complications. Fertility medicines and injections, germ cell tumors, molar pregnancy, and other variables can all impact an hCG blood test findings. See a doctor if you have any worries about testing your pregnancy early or had a miscarriage or fetal abnormality.
Infographic: Role Of Serum Beta hCG Test In Predicting Down Syndrome
Early prediction of fetal anomalies has several advantages. The beta hCG test, along with some other prenatal tests, can help identify Down syndrome at an early stage of pregnancy. The infographic below explains how the test results are interpreted to determine Down syndrome.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
Illustration: HCG Blood Pregnancy Test: How It Works & How To Detect Results

Image: Dall·E/MomJunction Design Team
Are you wondering what pregnancy test will give you the best results and which one you should opt for? Watch this video to learn all about a Beta HCG Test and how it can help diagnose pregnancy.
Personal Experience: Source
MomJunction articles include first-hand experiences to provide you with better insights through real-life narratives. Here are the sources of personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. Blood pregnancy test (May 8, 2014).https://myhappybirthjourney.wordpress.com/2014/05/17/blood-pregnancy-test-may-8-2014/
References
1. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG); Regents of the University of Michigan
2. HCG blood test – qualitative; U.S. National Library of Medicine, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
3. HCG blood test – quantitative; U.S. National Library of Medicine, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
4. Knowing if you are pregnant; Office of Women’s Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
5. Pregnancy Test (hCG); Lab Tests Online; American Association for Clinical Chemistry
6. Pregnancy testing; Better Health Channel; Department of Health & Human Services, Victoria State Government, Australia
7. HCG (Blood); University of Rochester Medical Center
8. HCG in Blood Serum — Qualitative; The Regents of The University of California; University of California San Francisco
9. How Is Gestational Trophoblastic Disease Diagnosed; American Cancer Society
10. Testicular Cancer Tumor Markers; The Johns Hopkins University
11. HCG blood test qualitative; Florida Agency for Health Care Administration
12. HCG – Serum, Quantitative; University of Iowa Diagnostic Laboratories
13. Pregnancy; U.S. FDA
14. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin; U.S. National Library of Medicine
15. HCG blood test – quantitative; Mount Sinai
16. Pregnant with twins; Raising Children Network
17. What is HCG?; American Pregnancy Association
18. Tips for Taking a Pregnancy Test Correctly; The Source
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Akanksha Allahbadia Gupta
Read full bio of Rebecca Malachi
Read full bio of Dr. Ritika Shah
Read full bio of Reshmi Das