Image: MomJunction Design Team

Making turkey part of your diet during pregnancy has never been easier and it can provide you with an adequate amount of protein which is sometimes a struggle. Even though turkey is rich in nutrients, knowing the right way to eat it is important to reap its health benefits safely.
Pregnant women are more prone to birth canal infection from listeria-infected turkey and it may also lead to pregnancy complications such as miscarriage. That is why it’s so important to pay attention to only thoroughly cooked meat. It is also recommended that you consume organically fed turkeys. These precautions can protect you from any adverse outcomes.
This post will tell you about eating turkey during pregnancy, including cooking tips, benefits, and potential side effects.
Key Pointers
- Turkey can help meet the protein requirements of a pregnant woman as it is a rich source of vital amino acids.
- It is also high in vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients.
- Consuming turkey during pregnancy carries a high risk of causing foodborne illnesses such as Campylobacter jejuni, Salmonella, and Clostridium perfringens.
- To avoid such risks, it is essential to properly wash, handle, and cook the turkey at accurate temperatures before consuming it during pregnancy.
Health Benefits Of Eating Turkey During Pregnancy
Let’s closely look at main health benefits of eating turkey while pregnant:
- Approximately 4 oz/115 grams of turkey contains around 32 gms of good quality protein and this helps meet higher protein requirements during pregnancy.
- Turkey is a good source of vital amino acids. A turkey sandwich can meet most of your protein requirements of the day.
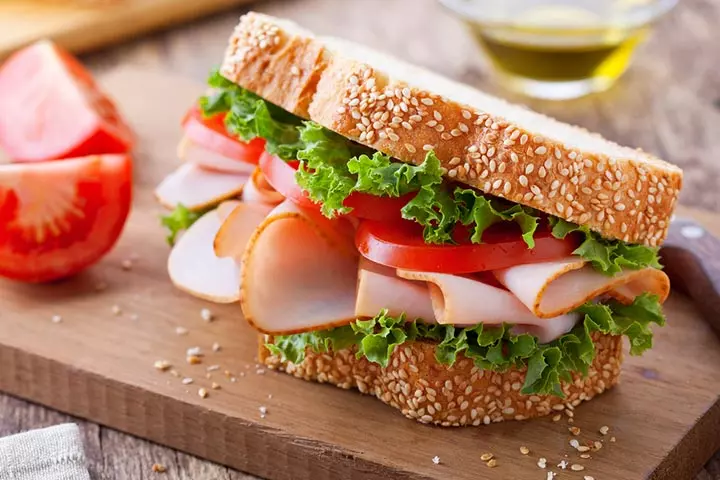

Image: IStock
- Turkey is a good source of B vitamins like B6 and B3 and minerals like selenium and phosphorus that you need for a healthy pregnancy
- If you want to get the best nutrients from your turkey, look for the ones that are raised under organic conditions.
- Turkey is a good source of folate and B vitamins like Vitamin B6, Vitamin B12, and Vitamin B3, and minerals like zinc, selenium, and phosphorus for a healthy pregnancy.
- For optimum nutrient intake from turkey, look for the ones that are raised under organic conditions.
Grass fed turkeys are rich in nutrients and much superior compared to the ones given antibiotics and with no access to the natural pasture. - Grass fed turkeys are rich in nutrients and much superior compared to the ones given antibiotics and with no access to the natural pasture.
 Health fact
Health factRisk of Contamination in Turkey
Turkey, like all poultry items, carry the risk of foodborne illness and the most common ones being Campylobacter jejuni, Salmonella, and Clostridium perfringens (1). This main concern could be prevented by following these two rules: First off, make sure to clean your hands thoroughly. To prevent spread of foodborne illnesses, it’s never recommended to wash the meat before cooking (2). Eating undercooked or contaminated meat can lead to Toxoplasmosis, a parasitic infection that could harm maternal health and the fetus. Second important consideration is the right handling and cooking temperatures. It’s recommended that this internal temperature when cooked be at least 75°C (3). This temperature can only be accurately measured using a culinary thermometer stuck into the thickest part of the meat. Contamination may also result from the following:
- Improper handling temperatures during storing, freezing, buying, etc which could prevent development of bacteria that might already be present in the meat.
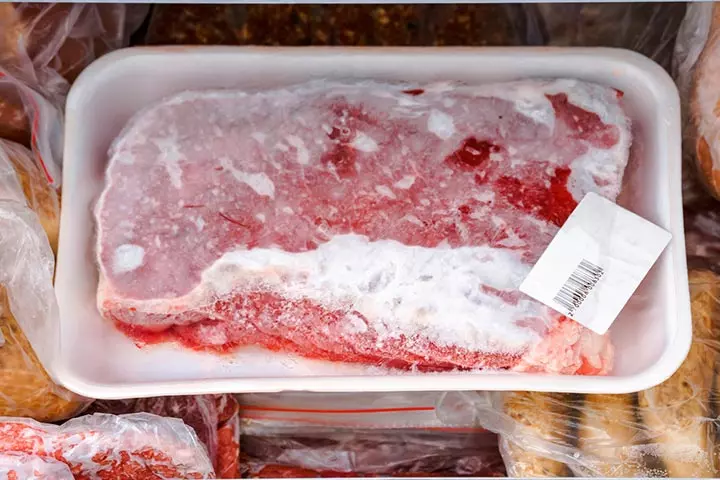

Image: IStock
- Listeria that crosses your placenta barrier and infects the birth canal multiples in the refrigerator as well, so refrigerating temperature has to be proper.
 Quick tip
Quick tip- If your turkey has any stuffing that was cooked inside the cavity, make sure that’s cooked at 75°C also.
Also, sourcing turkey meats from reputable sellers can also prevent the risk of contamination. These rules ensure turkey is perfectly safe for both you and baby.
According to the CDC, an outbreak of Salmonella Reading affected a total 358 individuals in 2019. Epidemiologic and laboratory evidence revealed that various types of turkey products from multiple sources were contaminated with Salmonella Reading, leading to illness among consumers. Therefore, it is crucial to be vigilant about the safety of turkey products and follow proper food handling and cooking practices to mitigate the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Some More Ways To Enjoy Turkey
There are so many fun ways to relish this superior source of protein in your diet to ensure protein adequacy, let’s look at a few below:
- Layer it to your sandwiches
- Top it on your pasta
- Make a curry with choice of spices
- Add it to soups or stews
- Grill it and use it in place of chicken to add variety
- Marinate it with different spice combos or use it in Mexican or Italian foods.
- Prepare turkey with some stir-fried vegetables for a healthy and nutritious meal.

Image: Shutterstock
Here are some food safety and dietary guidelines you need to keep in mind while cooking turkey:
- Buy fresh turkey mats, ideally sourced from organic farms.
- Buy store-packed turkey meats from a reputable source and check for proper packaging and expiration dates.
- Steady cooking is the best option.
- Cooking at a lower temperature means cooking for a long time.
- To get the best results, roast the meat at 300 degree Fahrenheit.
- Once the oven temperature reaches 140 degrees, you can increase the temperature to 400 Fahrenheit to brown the meat.
- To make sure the meat is cooked well, you can use an instant- reading thermometer.
- The best internal temperature to find out if the turkey is well cooked is internal temperature of 75 degree C degrees.
- While testing temperatures, make sure the thermometer does not touch the bone, as you will get wrong results this way.
- Keep the turkey in standby mode for 20 minutes so that it is done perfectly.
- If your turkey has any stuffing that was cooked inside the cavity, make sure that’s cooked at 75°C also. These rules ensure turkey is perfectly safe for both you and baby.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is cooked turkey breast safe during pregnancy?
Yes, turkey breast could be one of the safe foods to eat during pregnancy, provided it is cooked at an internal temperature of 165°F (4). A food thermometer can be used to check the internal temperature of cooked meat. Also, do not eat it every day. It is okay to eat in moderation and occasionally.
2. Can you eat turkey burgers while pregnant?
Yes, you can eat a turkey burger during pregnancy. However, ensure it is cooked well till it reaches an internal temperature of 165°F (4). You may avoid eating lettuce in the burger, especially when eating outside, to reduce the risk of infections from unwashed lettuce.
3. Can pregnant women eat Thanksgiving turkey?
Yes, turkey breast has a low-calorie count and a high protein content. Pregnant women can eat Thanksgiving turkey as long as it is fully cooked and free of harmful bacteria. They must avoid eating raw or undercooked meat, and smoked seafood to reduce the risk of foodborne illness.
4. Are turkey sausages safe to eat during pregnancy?
Yes, you can eat well-cooked turkey bacon as it is lower in calories and fat when compared to regular bacon (7).
Following these simple cooking tips will not only bring out the best taste of the turkey, but also ensure whether consumption of turkey during pregnancy is safe.
Having a balanced diet and following healthy eating patterns during pregnancy is very important. Eating a whole range of nutritious and wholesome food ensures proper health of your unborn. Make every bite of your food count. Choosing the right food has never been so easy once you have the right knowledge. Have a consultation with a nutritionist and seek accurate medical advice before adding this meat to your pregnancy diet.
Infographic: Delicious Turkey Recipes For Pregnancy
Turkey is a rich source of protein, an essential nutrition for pregnancy, and important vitamins. So with proper precautions, you may enjoy this delicious thanksgiving essential during pregnancy to support a healthy baby. Use the infographic below to find easy and tasty ways to include turkey in your diet.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntaxIllustration: Health Benefits Of Eating Turkey During Pregnancy
Image: Stable Diffusion/MomJunction Design Team
Master the art of preparing a turkey safely and reduce the risks of cross contamination while including this protein source in your pregnancy diet.
References
- Foodborne diseases of poultry and related problems;
https://www.sciencerepository.org/foodborne-diseases-of-poultry-and-related-problems_JFNM-1-105 - To Wash or Not to Wash.. Your Turkey?;
https://www.usda.gov/about-usda/news/blog/wash-or-not-wash-your-turkey - Indian Food Safety Requirements;
https://www.servsafeinternational.com/downloads/MK/Forms/pdf/EN.SSF.Intl.India.Food.Safety.Requirements.pdf - Cook to a Safe Minimum Internal Temperature
https://www.foodsafety.gov/food-safety-charts/safe-minimum-internal-temperatures - Nutrition During Pregnancy.
https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/nutrition-during-pregnancy - Food Safety; A Need-to-Know Guide for Those at Risk.
https://www.fsis.usda.gov/sites/default/files/media_file/2025-04/at-risk-booklet.pdf - Foods to avoid in pregnancy
https://www.nhs.uk/pregnancy/keeping-well/foods-to-avoid/
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Priyanka Sagar
Read full bio of Rebecca Malachi
Read full bio of Swati Patwal
Read full bio of Dr. Joyani Das
















