Image: iStock

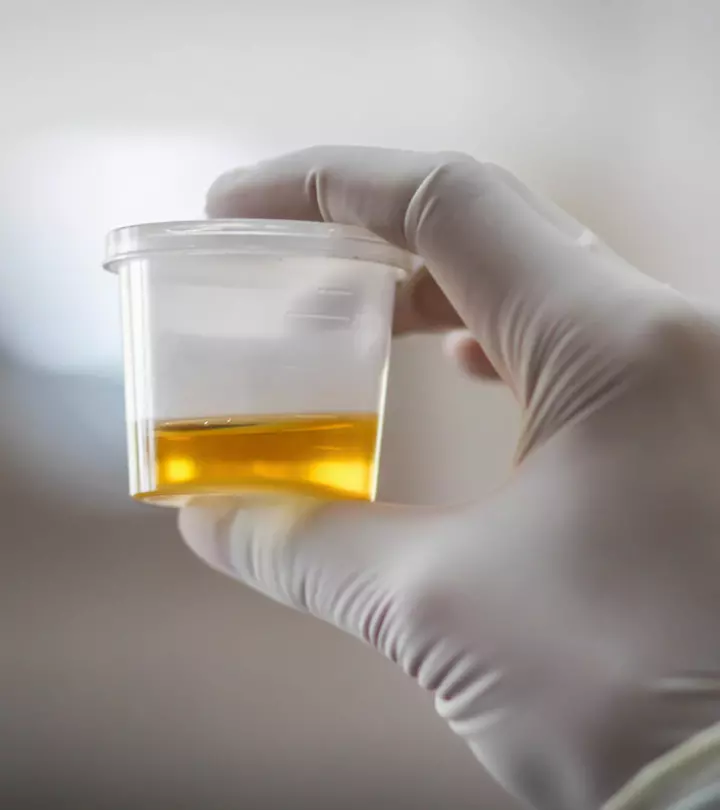
Uric acid is produced in the body during metabolic activities and later eliminated by the kidneys. However, there is constant fluctuation in the levels of serum uric acid in pregnancy. These fluctuations occur due to hormonal and renal blood flow changes. Hence, it is an important marker for fetal and maternal health (1).
Increased uric acid levels in pregnancy may indicate complications such as high blood pressure, gestational hypertension, and preeclampsiaiA pregnancy disorder characterized by high blood pressure, water retention, and protein content in urine (2). Read on to know more about the complications and management of elevated uric acid levels during pregnancy.
Key Pointers
- An increase in the level of pregnancy uric acid beyond 46.7mg/L is considered a sign of concern.
- High uric acid during pregnancy may increase the risks for premature birth and fetal and maternal complications.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and avoiding processed foods are some effective ways to prevent this condition in expectant mothers.
Normal Levels Of Uric Acid During Pregnancy
According to the Journal of Human Hypertension, the serum concentration of uric acid may remain at around 185μM (31.1mg/L) in the first trimester (2). However, the uric acid level increases as the pregnancy proceeds and may reach around 278μM (46.7mg/L) in the third trimester. This increase in serum uric acid concentration is common and not a sign of any disorder.
However, women with preeclampsia have a higher level of serum uric acid in the third trimester than women without the disorder.
Complications Of High Uric Acid Levels During Pregnancy
Image: Shutterstock
Some of the risks associated with high levels of uric acid during normal pregnancies are (1) (3) (4) (5):
- Higher risk of preterm birth and reduced time of delivery
- Risk of poor fetal prognosis and pregnancy outcomes in women
- Higher risk of lower fetal growth and lower birth weight
- Lower glomerular filtration rateiA test to examine the efficiency of kidney filtration by measuring the rate at which the blood is cleaned and reduced renal function
- Some studies suggest that elevated levels of maternal serum uric acid can cause hypertensive pregnancy. However, other reputed studies counter this argument, suggesting that although a high uric acid level signifies a complication, it does not contribute to it.
- Hyperuricemia (elevated uric acid levels in the blood) and hypertensive pregnancy may cause complications to the various organ systems in the body that can increase the risk of maternal morbidity during pregnancy.
- High uric acid levels can lead to maternal health complications, including endothelial injury and dysfunction.
- Uric acid crystal (urate) deposition in the joints can cause gout, a condition of painful joints. However, gout is rarely seen in pregnant women (6) due to elevated estrogeniA sex hormone responsible for the development of female sexual characteristics levels, which help remove uric acid.
Treatment Options For High Uric Acid Levels During Pregnancy
Image: Shutterstock
A study suggests that lowering the elevated serum uric acid level has limited benefits for gestational hypertension and preeclampsia (7). Thus, it is essential to maintain health parameters and lower serum uric acid levels for optimum prenatal care.
The following are some available treatment options for high uric acid conditions in pregnancy (8):
- Chronic hypertension can be managed using hypertensive medications. Regular checkups to maintain healthy blood pressure limits are crucial during pregnancy for hypertensive women, and immediate care is required if the blood pressure is >160/110 mm Hg.
- Preeclampsia in pregnancy may be treated with magnesium sulfate based on clinical signs of proteinuriaiAn elevated presence of proteins in the urine, which may indicate kidney damage and severe hypertension.
- Medications can be taken in consultation with your health care provider to reduce the elevated serum uric acid
Prevention Of The Complications Of High Uric Acid Levels During Pregnancy
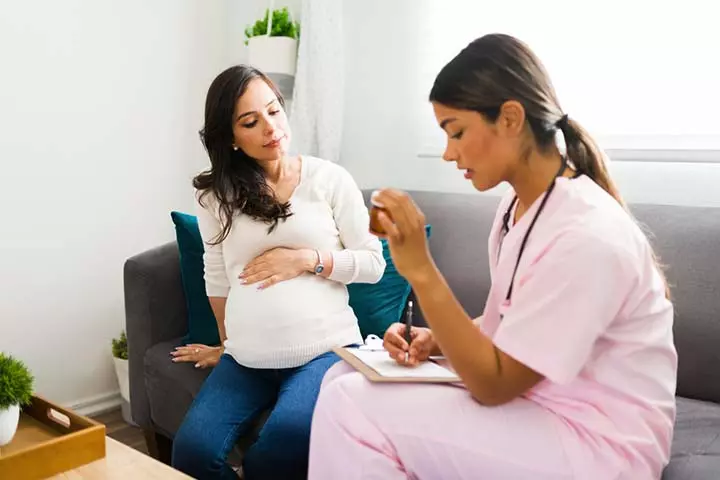

Image: Shutterstock
Increased serum uric acid may pose a risk of adverse complications for the mother and the fetus. Some of these complications can be prevented in the following ways (8):
- Fetal monitoring and ultrasound to check for growth constraints.
- Doctors may suggest preterm delivery based on the disease severity and clinical risk factors such as
- Repeated occurrences of severe hypertension despite regular monitoring and medication
- Thrombocytopenia or reduced platelet count
- Abnormal liver or renal function and renal disease
- Pulmonary edemaiSwelling caused by fluid retention in the lungs or cardiovascular risk factors
- Reduced fetal health and high risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes
Tips To Maintain Lower Serum Uric Acid Levels During Pregnancy
Elevated uric acid levels can be managed and prevented by maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Some steps to avoid high uric acid levels during pregnancy are (6) (9).
- Maintain a healthy weight by adhering to a strict exercise regime and diet plan.
- Keep diabetes in check with a healthy diet plan and reduce consumption of processed sugar and refined carbohydrates such as white bread.
- Consume vegetables and low-fat dairy products, and avoid purine-rich food such as red meat, poultry, oily fish, and seafood.
- Avoid saturated fatty processed foods and increase the intake of high fiber plant-based foods.
- If you do not have a renal problem, increase your fluid intake to remove the uric acid accumulated in the body.
 Research finds
Research findsFrequently Asked Questions
1. Can high uric acid cause miscarriage?
High uric acid levels and deposition in the joints could lead to gout (a rare condition in pregnancy causing pain and inflammation). Consequently, one study reported a possible association between gout in pregnancy and spontaneous abortion (the women in the study also had other complications). Hence, more studies are needed to prove this (10).
2. What level of uric acid indicates preeclampsia?
A study suggested that ⩽4.0 mg/dl uric acid levels as low, 4.1 to 6.0 mg/dl as a medium, and ⩾6.1 mg/ dl as high. Also, uric acid levels could be used to assess the severity of preeclampsia and management of pregnancy prolongation (11).
3. How can pregnant women monitor their uric acid levels?
A blood test, including a uric acid test, is usually recommended by doctors during pregnancy to examine uric acid levels (15).
4. Is there any evidence that high uric acid levels in pregnancy can cause congenital disabilities?
No, there is inadequate research to suggest that high uric acid levels could cause congenital disabilities in babies.
Uric acid levels are a vital indicator of the mother and fetal health. Generally, these levels keep fluctuating during gestation. However, an abnormal increase in uric acid levels may indicate an underlying issue, such as high blood pressure or preeclampsia. When uric acid excess happens, this metabolic byproduct builds up and leads to complications, such as reduced renal function and poor fetal growth. Thus, pregnant women should make healthy dietary and lifestyle changes to prevent high uric acid in pregnancy.
Infographic: Food That May Increase Uric Acid Levels When Pregnant
Certain foods may contribute to increased levels of uric acid. It is not advisable to completely avoid such foods during pregnancy owing to their nutritional benefits, but they may be consumed in moderation. The infographic below gives insights into the dietary factors that may influence uric acid levels.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
Some thing wrong with illustration image shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
During pregnancy, you may get a bought of gout. Find out in this video, with advice from experts on how to manage gout during pregnancy.
References
- Richard J Johnson et al.; (2011); Uric acid: A Clinically Useful Marker to Distinguish Preeclampsia from Gestational Hypertension.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3203211/ - Serum uric acid may not be involved in the development of preeclampsia.
https://www.nature.com/articles/jhh201547?proof=t - Shannon A Bainbridge and James M Roberts; (2008); Uric Acid as a Pathogenic Factor in Preeclampsia.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3319018/ - Uric acid and hypertension.
https://idp.nature.com/authorize?response_type=cookie&client_id=grover&redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.nature.com%2Farticles%2Fs41440-020-0481-6 - Wei Cai et al.; (2017); Uric Acid Induces Endothelial Dysfunction by Activating the HMGB1/RAGE Signaling Pathway.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5237466/ - Gout and Diet.
https://www.news-medical.net/health/Gout-and-Diet.aspx - Anna L Sampson; (2017); Uric acid-lowering therapies for preventing or delaying the progression of chronic kidney disease.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6485406/ - Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy.
https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.10803 - High uric acid or Gout – Causes, Prevention and Treatment.
https://www.narayanahealth.org/blog/high-uric-acid-or-gout-time-to-understand-it-better - Kevin Pierre et al., (2025); Gout in Pregnancy: A Rare Phenomenon.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7769799/#:~:text=Case%20reports%20suggest%20an%20association,demise%20%5B3%2C4%5D - A C Urato et al., (2011); Admission uric acid levels and length of expectant management in preterm preeclampsia.
https://idp.nature.com/authorize?response_type=cookie&client_id=grover&redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.nature.com%2Farticles%2Fjp2011187 - High Uric Acid Level.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17808-hyperuricemia-high-uric-acid-level - Shireen Meher et al.; (2014); Renal stones in pregnancy.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4934980/#:~:text=This%20leads%20to%20increased%20urinary - Pei-En Chen et al.; (2019); Effectiveness of Cherries in Reducing Uric Acid and Gout: A Systematic Review.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/337749692 - Uric Acid Test
https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/uric-acid-test/#:~:text=What%20is%20a%20uric%20acid
- Richard J Johnson et al.; (2011); Uric acid: A Clinically Useful Marker to Distinguish Preeclampsia from Gestational Hypertension.
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Shashwat Jani
Read full bio of Anshuman Mohapatra
Read full bio of Rebecca Malachi
Read full bio of Dr. Joyani Das

 Be watchful
Be watchful