Image: ShutterStock
Onlooker play is one of the six different stages of children’s participation in play, as Dr. Mildred Parten Newhall described. Onlooker play is characterized by the child being more engrossed in watching others play instead of participating themselves. You may encourage your child to play with others, but they refuse to participate and prefer only to be an audience and look. They prefer being observers of the different games their friends play. It is not unusual for parents to worry about their child losing interest in interacting with peers as they do not show interest in joining them for the play. Read this post to learn what onlooker play is and how it impacts children’s development as we explain in more depth with the help of some examples.

Key Pointers
- The onlooker play is one of the six stages of play and prepares children for social interaction.
- Although it may seem concerning to a parent, the onlooker play is an important stage in development.
- The transition from onlooker play to the next stage happens gradually. Arranging playdates or encouraging role play could assist this progress.
Does this scenario seem familiar to you?
If yes, you may have just witnessed an episode of onlooker play. You might worry that your child is losing interest in social interactions because they are not actively involved in the play. However, this may not be the case.
In this post, we talk about what onlooker play is, discuss some onlooker play examples, and tell you how it impacts your child’s development.
What Is Onlooker Play?
In 1932, sociologist Dr. Mildred Parten Newhall conducted a series of studies for her dissertationiA detailed documentation of an original research conducted by a person on a specific topic. and developed a system for classifying the stages of a child’s play that are crucial for your child’s social development.
According to Parten, there are six stages of social play that a child goes through, starting right from birth. As they experience each stage, they develop the social skills required to play with other children (1).
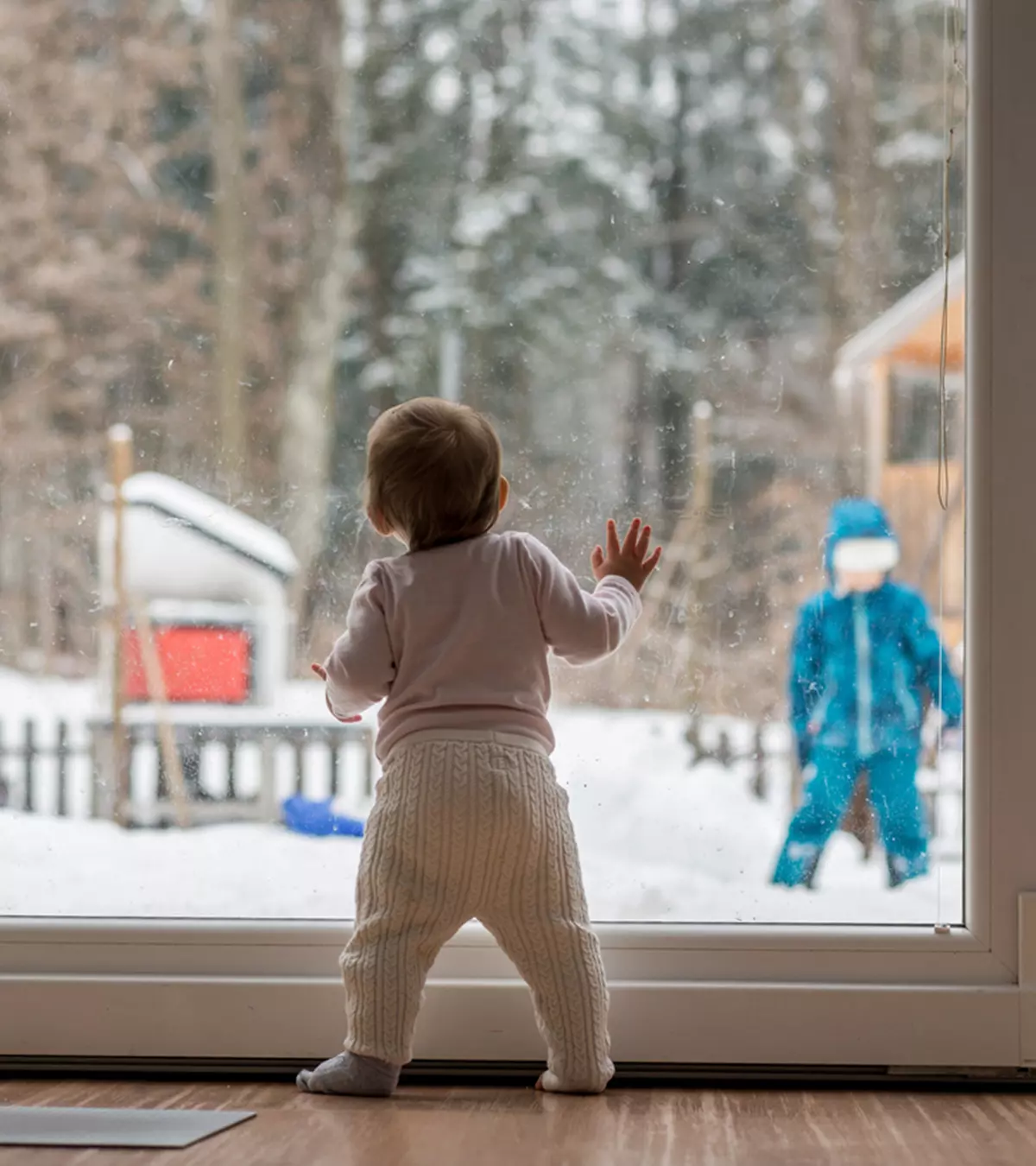
Onlooker play is one of the six types of play. It is when a child watches and observes other children playing but does not participate in the play. They prefer being a viewer or a watcher of the games other children play. This stage is essential as the child observes and learns from their surroundings. It is generally considered a preparatory phase for children to learn social interaction skills.
Let us now understand in brief what the six stages of social play are (2):
- Unoccupied play:This stage takes place from birth to three months of age. The baby moves their arms and legs and finds out how each part of their body moves.
- Independent play: This type of play begins from birth and lasts for two years. The child prefers playing alone and is not interested in playing with other children yet.
- Onlooker play: Also called spectator play, during this stage, the child observes other children playing but does not join them.
- Parallel play: This stage happens after the child turns two. In this stage, the child plays alongside others but does not participate in their play. As parents, there is no need to feel worried if your kids engage in parallel play because it is a part of their developmental process. According to Vi-Zanne, a mother of two girls, ”I panicked when my eldest just watched other kids play when she was first enrolled in daycare. She would play, but she was always in her own world. She didn’t seem to pay attention to other kids around her. I stumbled upon the concept of parallel play. It was then I realized that this is just a natural and important stage of my daughter’s development (i).”
- Associative play: This stage happens at around three years of age and continues till the child is four. In this stage, the child interacts with others during play but without the aim of achieving a common goal. You will also notice very little interaction and a lack of organization.
- Cooperative play: This stage occurs after the child turns four. The child develops an active interest in the activities of other children and participates in them. You will also notice cooperation, organization, and teamwork.
It is important to note that although the stages are described for children in the age group of 0–5, each child grows at their own pace, and they may not necessarily align strictly with the ages mentioned above.
Examples Of Onlooker Play Activities

Onlooker play doesn’t require any special set-up. It is an ongoing process that happens organically when your child is in the vicinity of same-aged or older children. If your child likes what they see, they will stop what they are doing and watch what others are doing. They will soak in new experiences by observing the activities of others around them.
Here are a few examples of onlooker play activities:
- Younger children in kindergarten watching the activities of older children
- Children who are slightly shy throwing in sudden suggestions in an activity they weren’t involved in
- A toddler observing the use of various pieces of play equipment in a play area
- Your child watching other children pretend play or dress-up
- Your child watching a children’s choir or play attentively
When Does Onlooker Play Begin?
Onlooker play usually occurs around two years of age and continues for up to six months or one year.
Usually, independent play and onlooker play happen simultaneously.
During this stage, it might seem that your child is missing out on social interactions and physical play. However, onlooker play is a milestone in terms of your child’s social development. Even if your child does not participate in the play, they view others and take mental notes. They not only survey how games are played, but also how different people interact with each other.
Why Is Onlooker Play Important?
Onlooker play is a crucial and beneficial stage in a child’s development. Even if the child seems passive and inactive when watching others play, their various brain functions are busily employed. It also helps develop their cognitive and social-emotional skills.
Cognitive skills
Watching others improves a child’s observation, perception, attention, and memory skills. They are also learning new words and more complex behaviors, such as gestures, which establish order in the play.
Social-emotional skills
Children learn by observing others. In the initial years, it is the primary caregiver, usually the mother. As they grow, their social circle increases, and they start observing other children to imbibe their characteristics. They try to imitate the mannerisms of the people they like and later try them out.
For children who are shy and reserved, onlooker play is a way to gain more experience without actually engaging with them. These children may benefit the most from onlooker play.
 Things to know
Things to knowPositives Of Onlooker Play

There are many positives of onlooker play. It could help your child
- Gain knowledge
- Observe interactions among other children
- Develop self-confidence
- Learn to cooperate with other children
- Develop their cognitive and social skills
- Develop their memory and deductive skillsiAbilities that help one think logically to derive at a fact-based conclusion.
How To Encourage Your Child During Onlooker Play?
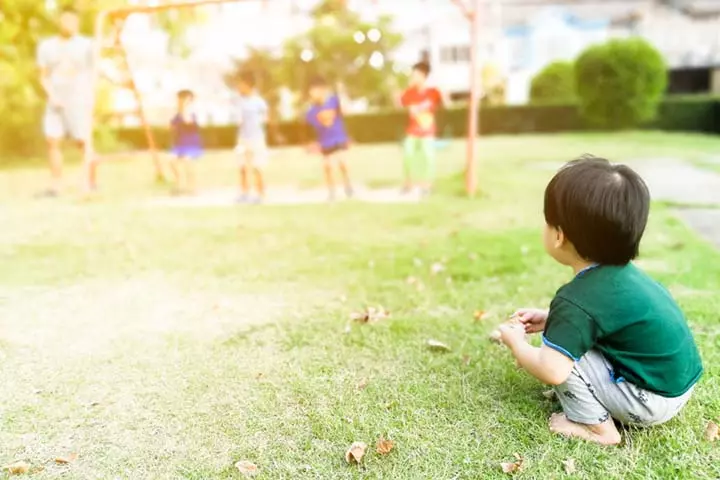

Parents always want their children to achieve the right milestones successfully. When you see your child watching others and not engaging with them, you might feel uneasy and emotional. But you have to remember that onlooker play is a crucial developmental stage, and your baby will soon transition to the next stage.
Parental presence can nurture their developmental skills and instill a belief in them that they can achieve the set targets. There are a few things that you can do to make the transition of your child to the next stage easy and smooth:
- Offer support to your child: When at the play area, switch off your phone and keenly observe what the child is doing. In some cases, if you participate in an activity or a game, it is more likely that your child will participate in it too.
- Encourage role play: Assemble a collection of old towels, toys, etc., in a place where your toddler can get their hands on whenever they want. Role play can help improve the imaginative and cognitive skillsiThe ability of the brain that helps one obtain, process, store, and use information correctly. of your child.
- Arrange playdates: Playing with children of a similar age could be a great learning experience for your child. They can also see adults (parents or babysitters) interacting with each other and learn social skills.
- Offer open-ended toys: Instead of giving them specific toys, give them open-ended toys, such as empty cartons or wooden blocks to play with. These toys can help them develop their imaginative and deductive skills, encourage freethinking, and improve their motor skills.
 Quick tip
Quick tipWhen Does Onlooker Play End?

When your child reaches 3–3 ½ years, they will move on to the next stage of play, that is, parallel play. In the parallel play stage, you will notice your child playing with other children. They might still not actively engage in play, but they will prefer playing alongside other children. They might probably share their toys, but they will play independently and won’t play to achieve a common goal.
 Quick tip
Quick tipWhen Should You Worry About Your Child’s Development?

If you feel your child hasn’t reached the onlooker play stage despite having reached an adequate age, there is no need to panic. They might be engaged in solitary play and may not notice what is happening around them. Some children can be quite reserved at a young age and slow in achieving their developmental milestones. These children might take some time to move on to the onlooker play stage (3).
If you have any concerns about your child’s development, do not hesitate to contact your pediatrician.
What Can You Expect Next?
As your child’s cognitive and social-emotional skillsiThe ability to understand, express and regulate one’s emotions and social behavior. develop, they will slowly transition into parallel play and then move on to associative play. Each stage comes with its own set of knowledge and learning, so be prepared to handle your child’s independence.
Every child has to achieve several developmental milestones while growing up. These milestones are important for your child’s mental, physical, social, and emotional development.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How can teachers incorporate onlooker play into their classroom activities?
Onlooker play involves a child watching others play. So, teachers may use onlooker play in the classroom to demonstrate certain activities or examples either performed by them for the students or their classmates.
2. Is onlooker play more common in certain cultures or communities?
Onlooker play might not differ in other cultures or communities. However, some cultures and communities may give more value to this play than others. For example, some parents may encourage their children to go out to socialize and play, while others may give time to their children to look and observe before preparing to join the social play.
Onlooker play is beneficial for children in multiple ways. However, you must know the right age to introduce it as it involves certain skills to be put to use. This play encourages motor development and allows the child to learn more about their social behavior. Thus, they must have the exposure and knowledge required so that they seek all the benefits that it has to offer. Once they understand the play, they can have fun around with their friends.
Infographic: Choosing Interesting Toys During Onlooker Play
Toddlers’ onlooker play begins at around two to three years when they watch and enjoy others’ playing. Although your child may not truly engage in playing, you may select intriguing toys and items to help them learn and develop. Read further as this infographic lists the toys that may interest your toddler during onlooker play.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
Illustration: Onlooker Play: Age Benefits Examples & How To Encourage It

Image: Dall·E/MomJunction Design Team
Children learn to play through Parten’s 6 Stages of Play: Unoccupied, Solitary, Onlooker, Parallel, Associative, and Cooperative. Let’s explore how each stage helps children learn to play!
Personal Experience: Source
MomJunction articles include first-hand experiences to provide you with better insights through real-life narratives. Here are the sources of personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. How to encourage parallel play in toddlers; WordPressReferences
1. How Kids Learn to Play: 6 Stages of Play Development; Pathways
2. The Power of Play – Part 1: Stages of Play; Michigan State University
3. Importance of Play in Children’s Development; Pathways
4. Onlooker Play; Children’s Museum of the Magic Valley
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Maymunah Yusuf Kadiri
Read full bio of Rohit Garoo
Read full bio of Dr. Ritika Shah
Read full bio of Apoorva K