Image: ShutterStock
Propranolol is a beta-blocker drug prescribed for the treatment of cardiac issues such as irregular heart rate and hypertension (1). Propranolol during pregnancy is seldom prescribed since beta-blockersiA class of drugs that help protect the heart by blocking some hormone effects and reducing heart activity. may pose a risk to the developing fetus. The drug may be prescribed as a last resort when other medicines yield no results. You must consult your doctor before consuming propranolol or other beta-blockers to minimize possible side effects. Read on to know about the medication safety of using propranolol during pregnancy, the dosage instructions, side effects, and dosage precautions that should be kept in mind.
You must consult your doctor before consuming propranolol or other beta-blockers to minimize possible side effects. Read on to know about the medication safety of using propranolol during pregnancy, the dosage instructions, side effects, and dosage precautions that should be kept in mind.
Key Pointers
- Propranolol is a beta-blocker drug used for treating abnormal heart rhythms, high blood pressure, anxiety, and migraines.
- It is not commonly prescribed during pregnancy as it can be risky for the fetus.
- Common side effects include slow heart rate, low blood pressure, dizziness, blurred vision, tiredness, weakness, and sleeping problems.
- If any side effects occur, stop taking the drug and consult a doctor.
- Propranolol should only be taken if the potential benefits are greater than the risks.
What Is Propranolol?
Propranolol (Innopran XL) is a beta-blocker that is used to treat high blood pressure, anxiety, and migraines (2).
Propranolol can especially help in (1):
- Treating irregular heartbeats
- Preventing future heart attacks, and cardiovascular diseases such as strokes
- Preventing chest pain due to angina
- Treating hypotension (high blood pressure)
- Preventing episodes of reduced blood flow to the heart muscle (Acute Ischemic Attacks).
- Reducing involuntary shaking (tremors)
- Managing symptoms of performance anxiety
It also helps in reducing symptoms of excessive thyroid hormone in the body. It is available in tablet, capsule, and liquid form.
Is It Safe To Take Propranolol During Pregnancy?

The US Food and Drug Administration has categorized propranolol under “pregnancy category C.” This means animal studies have shown that the drug has adverse effects on the fetus, and there are no well-controlled studies in pregnant women (3). Therefore, the existing research considers propranolol to be among the medications to avoid during pregnancy.
While gestational hypertension and cardiac issues can make pregnancy risky, taking medication that can harm your baby is not a good idea. As there are no well-controlled studies in pregnant women and the available studies suggest adverse effects of propranolol on the developing fetus, this drug should be taken during pregnancy only if the potential maternal health benefits outweigh the risks and strictly under the guidance of your physician.
How Does Propranolol Affect Pregnant Women?
An animal study on rats found that oral administration of propranolol through pregnancy led to reduced neonatal weight and litter size. In humans, the observations could be interpreted to the increased muscle tone of the uterus, and instability in blood flow (4). A study report states, “ Exposure to β-blockers during pregnancy was associated with being born with SGA, preterm birth and perinatal mortality (5).”
Mothers who were given propranolol Hcl at the time of labor showed signs of bradycardia (slow heart rate), hypoglycemia, and/or respiratory depression (3). Talk to your doctor and discuss if there are any safer alternatives to propranolol.
Recommended Dosage

The US FDA recommends the following doses for each condition (6). However, your doctor will decide the dosage after considering your requirements (7).
- The recommended dosage for hypertension is 40mg twice a day, and it is not known to cause any adverse effects during pregnancy.
- Although the FDA recommends 80mg-320 mg for angina pectorisiFeeling squeezing, heaviness, pressure, or tightness in the chest due to reduced blood supply to the heart. , studies proved that a dosage of more than 160 mg could cause adverse effects on the fetus. So, professional advice is needed.
- Up to 30mg three or four times daily for atrial fibrillationiAn irregular heart rhythm that initiates in the upper chambers of the heart.
- The initial dosage for myocardial infarctioniInterrupted blood flow to cardiac muscles, widely known as heart attack. is 40mg, and after one month, it can be 60mg to 80mg.
- Initial dosage for migraine may range from 20 to 80mg, 3-4 times a day; it should be taken after consulting a medical professional.
 Quick tip
Quick tipWhether taken in the prescribed dosages or otherwise, propranolol can have certain side effects in the patients.
Side Effects Of Propranolol During Pregnancy

Propranolol has some common side effects on the mother (8).
- If the mother has an intolerance to propranolol tablets, then she could experience a slow heart rate, low blood pressure, dizziness, light-headedness, blurred vision.
- A few common side effects include tiredness, weakness, cold extremities, difficulty in sleeping, irregular heartbeat, Raynaud’s syndromeiA medical condition characterized by blood vessel spasms due to cold temperatures or emotional stress. , and nightmares.
If you do take propranolol during pregnancy and experience any of these symptoms, then stop taking the medication and contact your obstetric specialist or gynecologist immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is it okay to take propranolol occasionally during pregnancy?
Do not take propranolol occasionally, as the withdrawal of the medicine from your system should be gradual, over 10 to 14 days. You may experience unpleasant side effects such as sweating, shaking, worsening of angina, irregular or fast heartbeat, heart attack, or even death in some cases (8).
Also, medications for hypertension and anxiety need to be taken continuously for a certain period. So always discuss with your doctor before starting or stopping the medication and stick to the prescribed dosage.
2. What if I have already taken propranolol during pregnancy?
So, if you are already under medication, and found out that you are pregnant, then talk to your doctor to decide the best course of action, as abruptly stopping the drug is not safe.
3. Can propranolol cause miscarriage?
Several studies did not include miscarriage as an adverse effect of propranolol (9). However, the lack of well-controlled studies makes it difficult to determine if propranolol causes miscarriage.
4. Can taking propranolol during pregnancy cause stillbirth?
A study conducted based on the data from the Danish Fertility Database, the Danish National Hospital Register, and the National Prescription Register found that a higher rate of perinatal mortality was found among women exposed to beta-blockers (10). So, there is a chance of stillbirthiWhen a fetus passes away in the uterus or is born dead after 20 weeks of pregnancy. upon the usage of propranolol during pregnancy.
5. Can taking propranolol during pregnancy cause any birth defects?
A paper published in The Journal of Pediatrics states that infants born to mothers who received continuous propranolol therapy during pregnancy reported a small placentaiA temporary organ that develops during pregnancy and provides the fetus with oxygen and nutrients. , fetal growth restriction or intrauterine growth retardation, fetal depression at birth, neonatal hypoglycemia, and bradycardia (5) (6).
6. What is the safest beta blocker in pregnancy?
The beta blocker, labetalol, is usually prescribed for the treatment of gestational hypertension, while metoprolol is the most commonly used for arrhythmias, cardiomyopathies, and aortopathies. Your doctor will decide the best medicine for you based on your overall health and medical requirements (11).
7. Does propranolol cross the placenta?
Yes, beta blockers such as propranolol are known to cross the placenta (12).
8. Can Propranolol interact with other medications during pregnancy?
Yes, it may interact with OTC medicines, such as antacids that contain aluminum, cimetidine, and NSAIDs, such as naproxen and ibuprofen (13). Do not start any new medications while on Propranolol without first consulting your healthcare provider.
9. Are there specific health conditions that could complicate Propranolol use in pregnancy?
Propranolol use during pregnancy requires careful medical supervision as Propranolol use can be complicated by pre-existing conditions such as asthma, cardiac conditions such as irregular heartbeat and heart failure, and lung disease (13).
Propranolol is a beta-blocker usually prescribed for conditions such as high blood pressure, migraine, and anxiety. The doctor may perform a risk assessment and prescribe it to you if they find that the benefits outweigh the risks. However, there are not enough studies done on humans to establish the safety of propranolol in expecting mothers for treatment of the pregnancy problems such as preeclampsia. In addition, research on animals has shown adverse effects on the fetus, and therefore you should not take propranolol during pregnancy without your doctor’s consent.
Infographic: Side Effects Of Propranolol During Pregnancy
Your doctor may have advised taking propranolol when pregnant for a medical reason; though the drug may not harm your fetus, it could cause certain discomfort to you. This infographic discusses the possible side effects of propranolol during pregnancy. Make a note and inform your doctor if you notice any of these symptoms. Illustration: Momjunction Design Team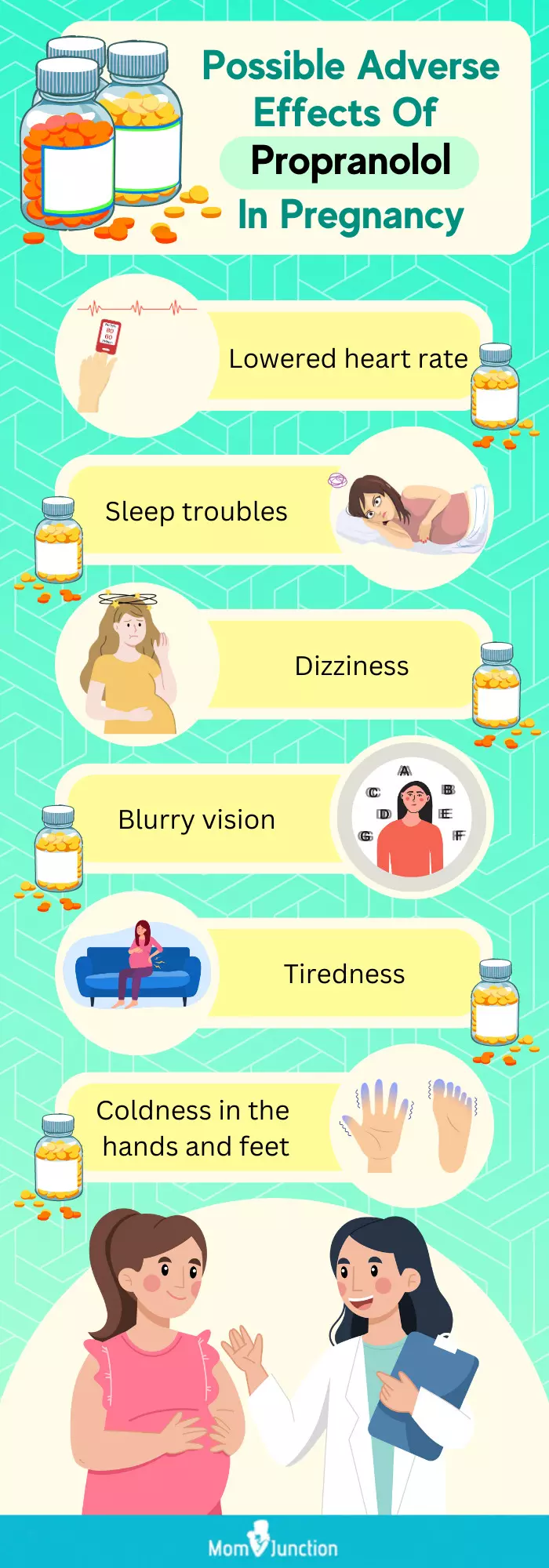
This post is for informational purposes only and is not a replacement for a doctor’s consultation. Do not use any medication without talking to your doctor.
Get informed about propranolol usage, proper dosage, and possible adverse effects from a physician. Acquire the necessary knowledge to make well-informed choices regarding your health.
References
- Propranolol.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557801/ - Propranolol.
https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/propranolol/ - Prescribing Information-Innopran XL.
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/021438s016lbl.pdf - N. Schoenfeld et.al; (1978); Effects of Propranolol during Pregnancy and Development of Rats. I. Adverse Effects during Pregnancy.
https://www.nature.com/articles/pr19781512.pdf?origin=ppub - Kasper Meidahl Petersen et.al; (2012); β-Blocker treatment during pregnancy and adverse pregnancy outcomes: a nationwide population-based cohort study.
https://bmjopen.bmj.com/content/bmjopen/2/4/e001185.full.pdf - M.D. Gwendolyn R. Gladstone et.al; (1975); Propranolol administration during pregnancy: Effects on the fetus.
https://www.jpeds.com/article/S0022-3476(75)80236-8/abstract - Inderal.
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2011/016418s080016762s017017683s008lbl.pdf - E A Taylor and P Turner; (1981); Anti-hypertensive therapy with propranolol during pregnancy and lactation.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2424946/ - Propranolol.
https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/files/pil.11811.pdf - Mohammad Y Yakoob et.al; (2014); The Risk Of Congenital Malformations Associated With Exposure To Beta-Blockers Early In Pregnancy: A Meta-Analysis.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4086784/ - Beta-Blockers in Pregnancy and Congenital Malformation Risk.
https://www.acc.org/Latest-in-Cardiology/Journal-Scans/2018/11/28/10/13/Beta-Blocker-Use-in-Pregnancy-and-the-Risk-for-Congenital - Lewei Duan et.al; (2017); β-Blocker Exposure in Pregnancy and Risk of Fetal Cardiac Anomalies.
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2618817# - Propranolol (Cardiovascular).
https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a682607.html
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Arpita Chakraborty
Read full bio of shreeja pillai
Read full bio of Rebecca Malachi
Read full bio of Dr. Joyani Das