Image: Shutterstock
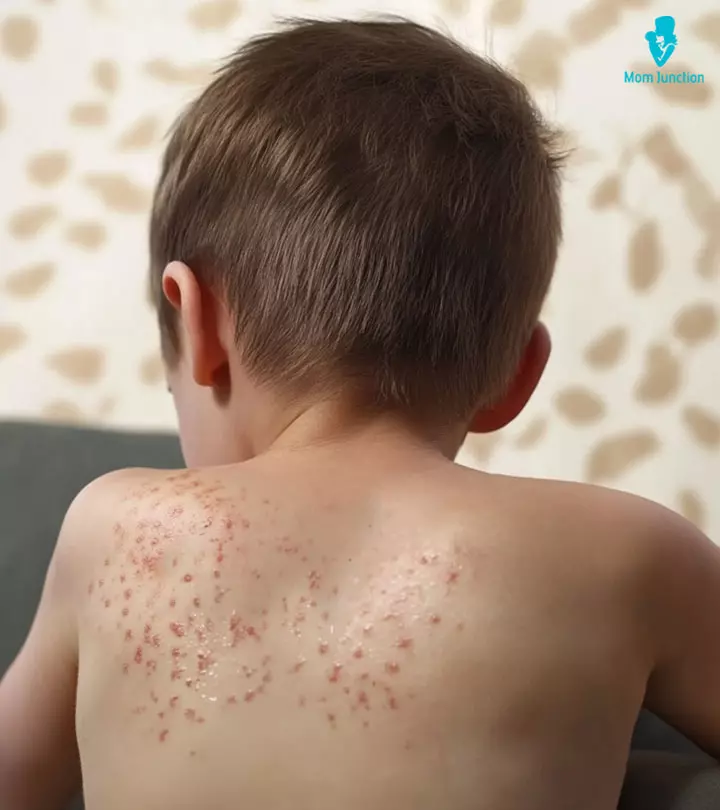
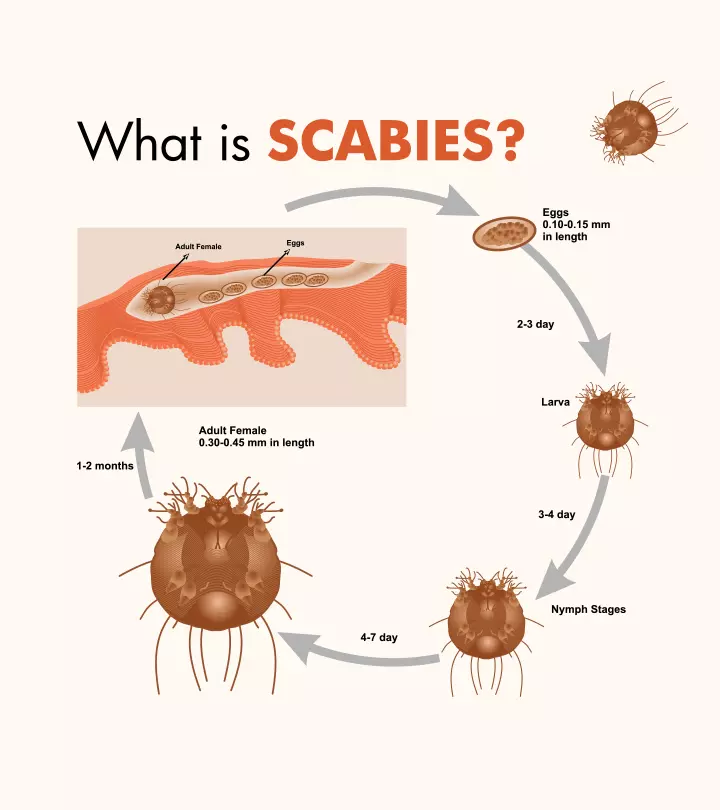
Scabies in kids is caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabei var hominis. The mite creates burrows in the human skin for reproduction. When affected by Sarcoptes, the skin turns hypersensitive, and the body’s immune response gives rise to uncomfortable, itchy pimple-like rashes and blisters on the skin (1). Scabies spread quickly in public places, making children more susceptible to it. Thus, even if one child catches scabies in the neighborhood or school, it puts the other children and their families at risk of contracting it. Recognizing and treating it early can prevent it from spreading and causing more problems. Read on to learn about the causes of scabies, risk factors, symptoms, complications, and treatment for scabies in children. We also tell you about the measures to prevent the spread of infection.

Key Pointers
- Scabies is a mite-caused infection that presents with typical itchy rashes and blisters in various body parts of a child.
- Topical creams and ointments are effective in treating scabies.
- If left untreated, scabies could lead to serious conditions, like sepsis.
- To prevent scabies, seal soft toys in plastic bags to starve mites, avoid contact with infected people, and do not let your child out if they are diagnosed with scabies.
Is Scabies Contagious?
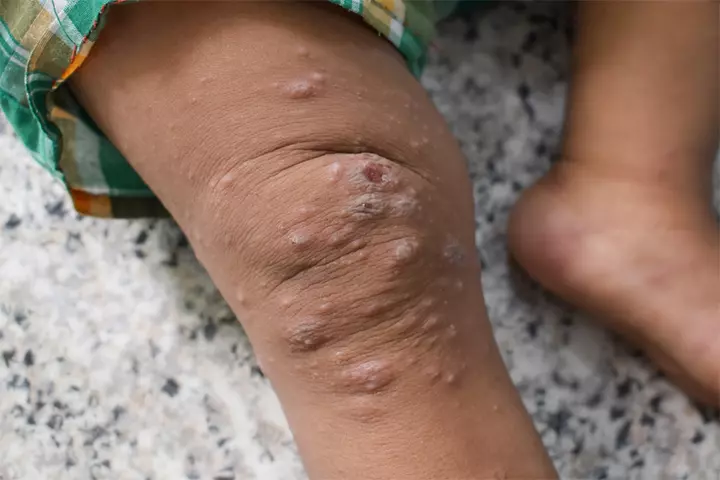
Yes, scabies, a parasitic infection, is a highly contagious disease that spreads through skin-to-skin contact. Thus, children who come into contact with a child who has an infestation at school or childcare center are at a high risk of getting scabies (2).
A child could also get scabies by sharing clothes, utensils, bed linens, or toys with another child who has an infestation. The mites could survive on non-living items for two to three days. Thus, even one person with scabies can cause a scabies outbreak in an area (3).
What Are The Causes And Risk Factors For Scabies?

Scabies is a skin infestation caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei var hominis. The scabies mites bury themselves under the skin to lay eggs. This scabies infestation triggers the body’s immune system and causes skin inflammation, redness, itchiness, bumps, and skin rashes in children (4) (5).
Each year, approximately 300 million people worldwide are affected by scabies (6). The prevalence of scabies is closely linked to poverty, malnutrition, homelessness, and inadequate access to hygiene. Recognizing its widespread impact, the WHO classified scabies as a neglected skin disease in 2009 (6).
All children are at risk for scabies as they tend to be in group settings. Poor hygiene and overcrowded living conditions also pose a risk for scabies. According to the World Health Organization, 5% to 50% of children living in such conditions are prone to getting scabies (7). Children with compromised immunity may show a severe reaction towards it (3) (5) (7).
What Are The Symptoms Of Scabies?
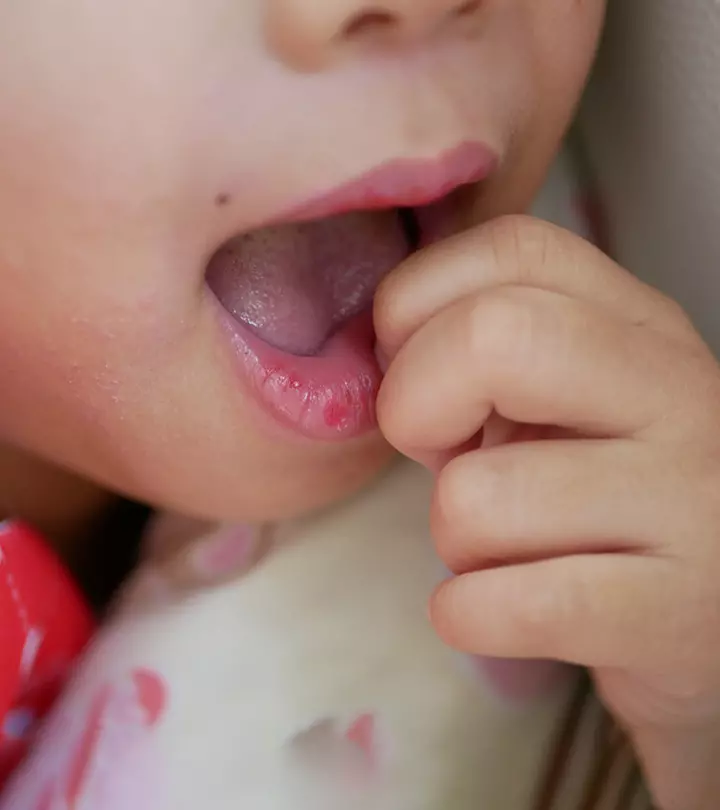
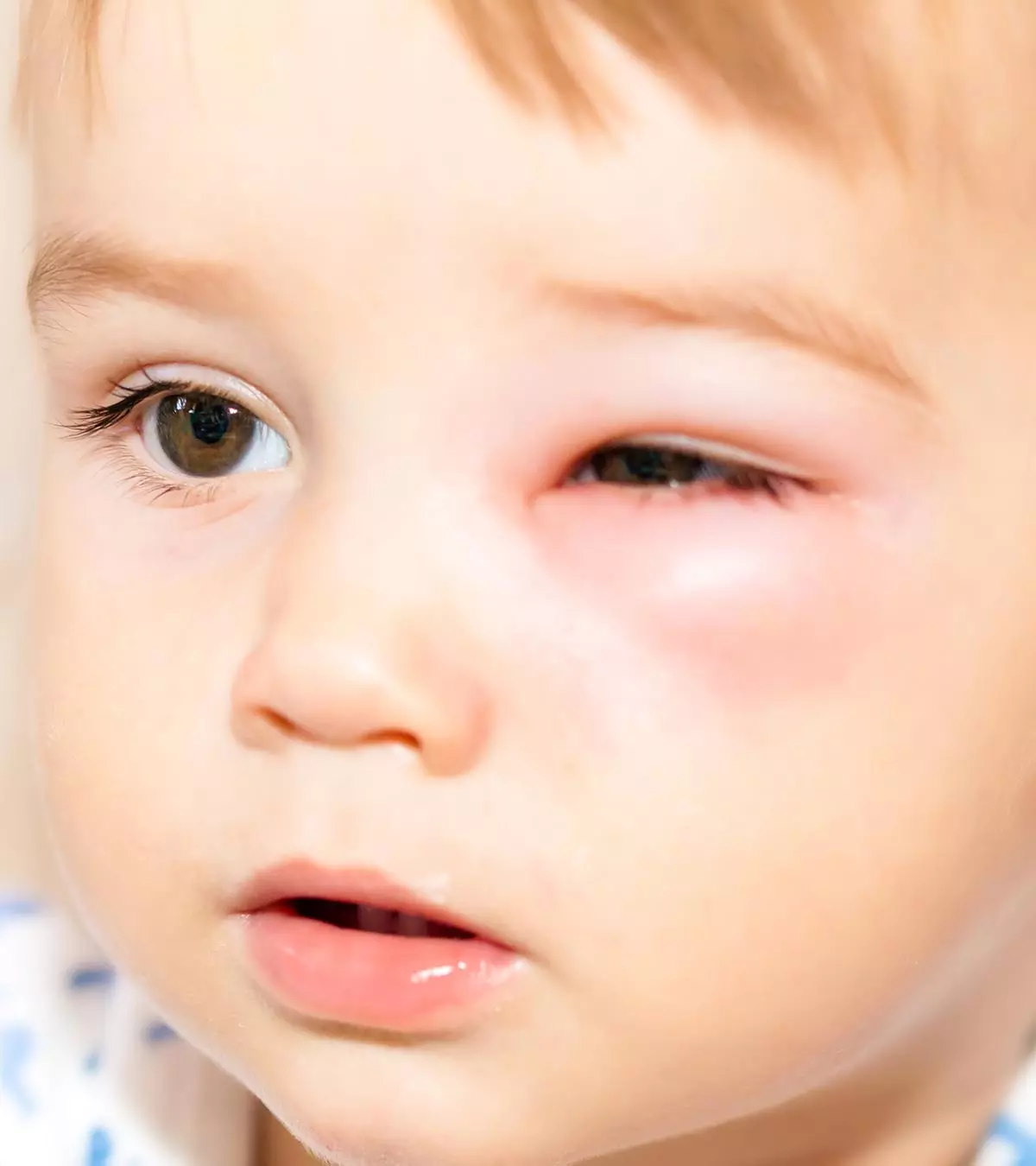
The symptoms of scabies may appear four to six weeks after the child comes into contact with an infected person. Itchy rashes, pimples, and blisters are the common symptoms of scabies. The infestation may also cause burrow tracks, which are raised, thread-like lines on the skin. The skin may sometimes become thickened, scratched, or scabbed due to continuous itching. Young children may also show signs of irritability and poor feeding (8). The common itchy and affected regions for scabies in children include the following (2).
- Between the fingers
- Armpits
- Wrists
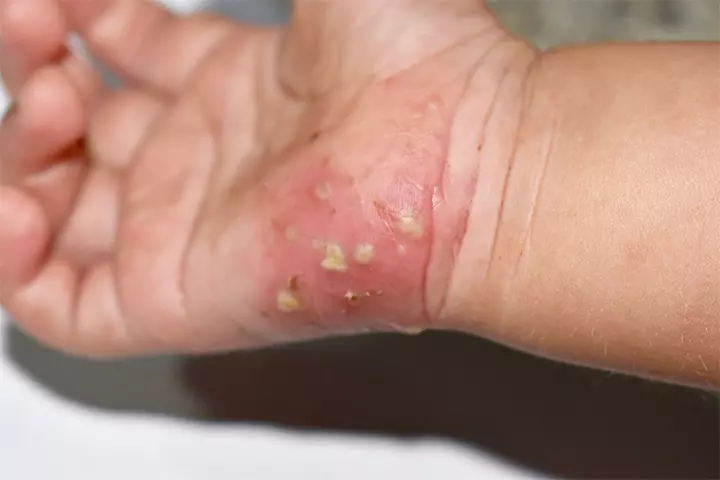
The intensely itchy sensation may increase at night or after a hot water bath.
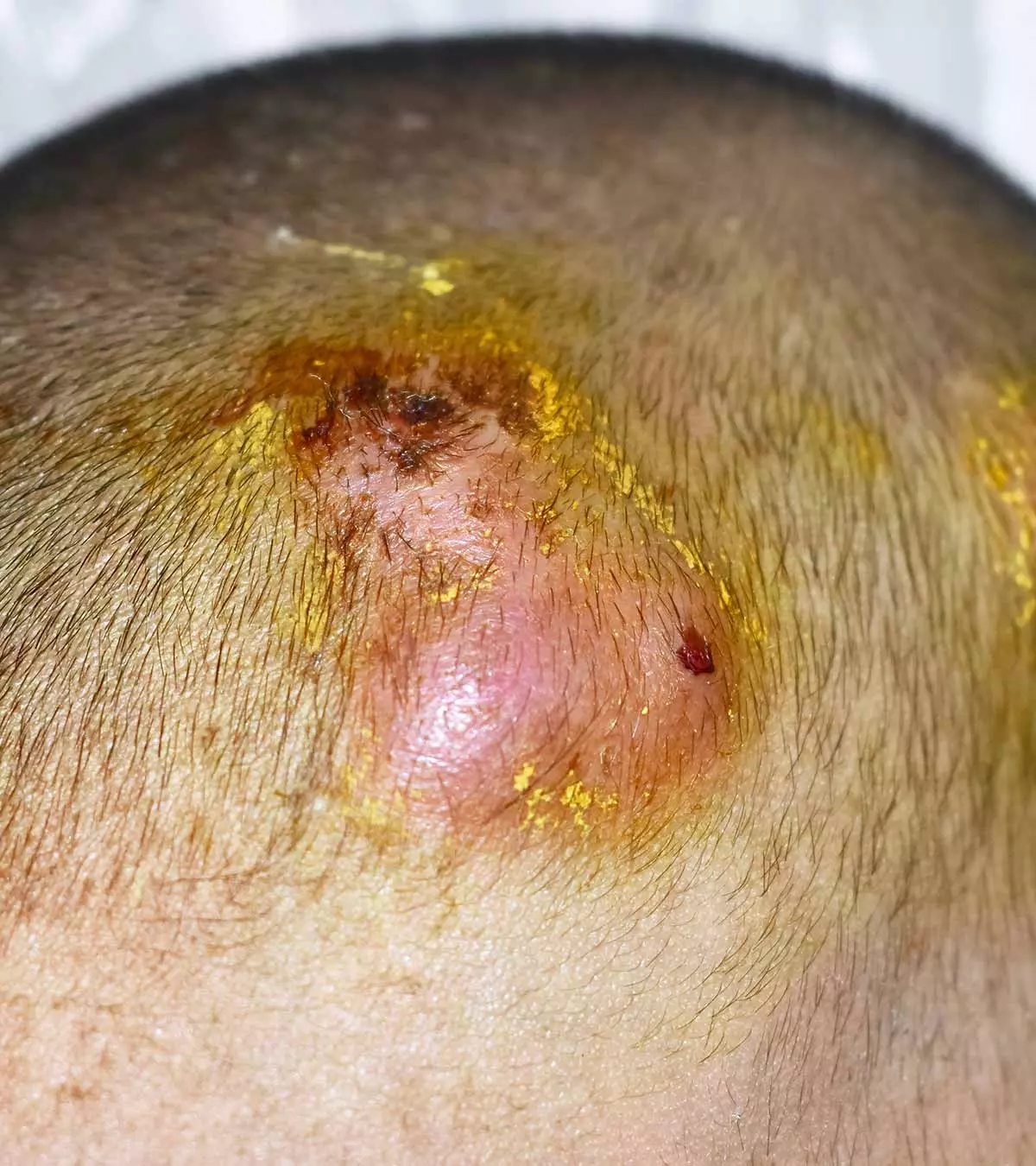
In some rare cases, crusted scabies, which are characterized by widespread scale and crust, may be seen in children with a weak immune system. Children with crusted scabies require immediate medical care (1).
 Quick fact
Quick factWhat Are The Complications Of Scabies?
If left untreated, scabies can lead to adverse complications. Persistent scratching can break the skin, making it vulnerable to bacterial infections such as impetigo. Streptococcus pyogenes, the bacteria responsible for impetigoiA highly contagious bacterial skin infection that causes red sores which rupture, ooze fluid, and develop honey-colored crusts , has been linked to conditions like rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease (7).
The intense itch caused by the scabies rash could lead to severe skin sores. Also, untreated scabies may attract several bacteria, particularly Staphylococcus aureus. This can lead to skin infections such as sepsisiAn extreme and overactive bodily response to an infection of the skin (1).
Scabies infestations can also trigger acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, a kidney condition that develops after a Streptococcus infection. Recurrent scabies infestations are also common, especially in crowded living conditions or when treatment is incomplete (7).
 Quick fact
Quick factHow Is Scabies Diagnosed?
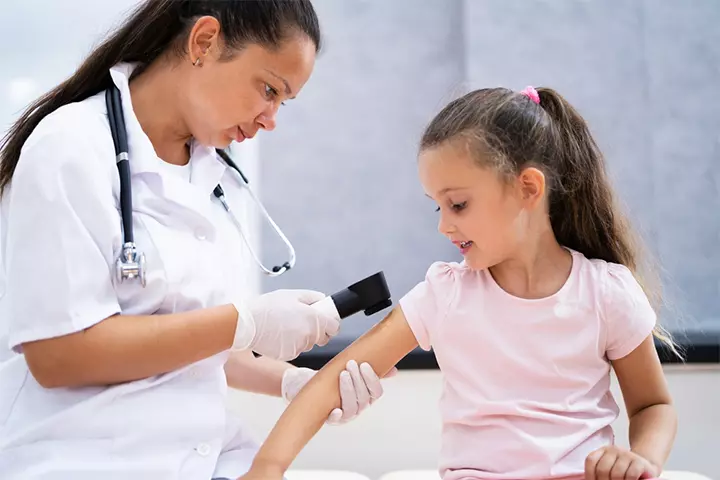
Diagnosing scabies involves a physical examination followed by a microscopic analysis of the skin and a review of the patient’s medical history. Your child’s healthcare provider may closely examine the rash and look for signs of burrow tracks or other characteristic symptoms. In some cases, a painless skin scraping may be performed. It involves gently removing a small skin sample to examine it under a microscope and checking for mites, eggs, or fecal matter (2).
A non-invasive technique called videodermatoscopy can also be used during the physical examination. This method involves a video camera with high magnification and optical fibers, allowing a detailed view of the affected skin. If the diagnosis remains unclear, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the presence of scabies mites (6).
What Is The Treatment For Scabies?

Effective treatment for scabies primarily focuses on killing the parasite while simultaneously healing the skin. A Scabicide cream, primarily Permethrin (5%), is usually prescribed for scabies in children older than two months of age. Other common medications administered for scabies include crotamiton cream (10%), benzyl benzoate lotion (25%), sulfur ointment (5-10%), and lindane lotion (1%).
The most common side effect of benzyl benzoate is skin irritation after a few minutes of application. Therefore, do a patch test before application and report to your doctor if you have an allergy. Spinosad 0.9% liquid is a newer treatment for scabies. Originally approved for treating head lice, it is now also approved for scabies treatment in patients four years and older (10).
Oral ivermectin is another treatment option, particularly for older children and adults. While not FDA-approved for scabies treatment in the U.S., it is commonly prescribed for individuals over ten years old. For individuals with severe scabies or those who do not respond to initial treatments, additional options include topical malathion and topical ivermectin (6).
The healthcare provider may also prescribe antibiotics and antihistamines to fight bacterial infection and help the child manage the itch (10) (11) (12).
 Quick tip
Quick tipSelf-Care Tips For Managing Scabies In Children At Home
Dealing with scabies in children can be difficult, but you can follow some effective home care strategies to help them. These tips aim to ease symptoms, support healing, and stop the spread of scabies (13) (14).
- Keep the infected area clean and dry.
- Trim your child’s fingernails short to avoid scratching and minimize skin damage, which can help reduce the risk of secondary bacterial infections.
- Apply cool compresses to relieve itching.
- Give your child a cool or lukewarm bath for about ten minutes to ease intense itching.
- Use over-the-counter antihistamines to help reduce itchiness.
- Wash all items your child has worn or used in the past week in hot water and dry them at a high temperature. This should be done on the day treatment begins.
- Reapply the medicine to their hands if your child washes their hands after applying the prescribed cream or lotion. It is vital as mites often burrow between the fingers.
- Continue following the full treatment course even if symptoms improve.
- Consider loose-fitting cotton clothing to reduce skin irritation and allow the skin to breathe.
Can Scabies Be Prevented?
Scabies is a highly contagious parasitic infestation. So, preventing it altogether may not be possible. Nevertheless, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggests the following measures to reduce the spread of scabies among children (7) (15).
- Avoid skin-to-skin contact with an infected person.
- Machine-wash all the clothes and bed linens used three days before the diagnosis of scabies. Ensure that these items are hot-water washed separately and dry-cleaned.
- Seal non-washable items such as soft toys in a plastic bag and leave them for three days to starve the mites.
- Avoid sharing personal items such as clothing, towels, and bedding with family members during an outbreak.
- Vacuum carpets, rugs, and upholstered furniture to remove any mites that may have fallen off the skin.
- Do not send children with scabies to school for about a week.
- Educate children about the importance of personal hygiene and not sharing personal items in school settings.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Where does scabies usually start?
Scabies usually develops in the body crevices, such as the beltline and the area around the nipples, penis, and buttocks (16).
2. Can scabies go away on their own?
No, scabies does not resolve on its own but requires treatment to stop the spread and alleviate the symptoms (17).
3. Does calamine lotion work for scabies?
Dr. Neema Shrestha, a consultant pediatrician and neonatologist, says, “People infected by scabies can have severe itching, making it difficult for them to perform daily activities. Since calamine lotion has a soothing and antipruritic action on the skin, it can help alleviate itching caused by scabies. It is also considered safe in children and small babies.”
4. How can parents access resources and support for managing scabies in their children?
Parents can seek help and support in managing scabies in their children by reaching out to their child’s pediatrician or healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
5. Which soap is used for scabies in babies?
The treatment of scabies in babies typically involves medicated creams or lotions instead of using specific soaps. Consult a healthcare provider for proper guidance on specific soaps to treat scabies in children.
6. How long does it take for scabies treatment to work in children?
Treatment for scabies in children generally starts working in a few days, but it may take two to four weeks for all symptoms to disappear. The primary treatment is a cream or lotion that kills the mites. You may apply it to your child’s entire body and leave it on for eight to 12 hours before washing it off (13). It’s normal for itching to persist for some time after treatment, but this doesn’t mean the treatment wasn’t effective. If symptoms do not improve after four weeks, consult your doctor again.
Scabies in kids is a contagious disease that spreads rapidly in public places. Wrists, armpits, the chest area, groin area, thighs, buttocks, and private parts are more commonly affected. Scabies can lead to complications such as skin sores, and if untreated, it can also result in sepsis of the skin and rheumatic heart disease. Scabies can be treated through medications, creams, and antibiotics prescribed by a doctor. Further, the preventive measures suggested by the CDC will help prevent the spread of this disease among children.
Infographic: Home Management Of Scabies In Children
Scabies needs management and does not self-resolve. Check out this infographic, where we enlist some effective, medically researched, safe home remedies for scabies. Consult your doctor before trying these home remedies for children.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
Illustration: Scabies In Kids: Causes Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment

Image: Dall·E/MomJunction Design Team
Scabies is a contagious infection in children caused by parasites. Watch this video to gain insights into the signs, diagnosis, causes, and treatment.
References
- About scabies.
https://controlscabies.org/about-scabies - Scabies in Children.
https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content?ContentTypeID=90&ContentID=P01921 - Scabies in Children.
https://www.stanfordchildrens.org/en/topic/default?id=scabies-in-children-90-P01921 - About Scabies.
https://www.cdc.gov/scabies/about/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/scabies/index.html - Scabies: Who gets and causes.
https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/scabies-causes - Scabies.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544306/ - Scabies.
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/scabies - Scabies.
https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/scabies.html - Scabies.
https://raisingchildren.net.au/guides/a-z-health-reference/scabies - Scabies: Diagnosis and treatment.
https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/scabies-treatment - Lina Albakri and Ran D. Goldman; (2010); Permethrin for scabies in children.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2954078/ - Treatment of Scabies.
https://www.cdc.gov/scabies/treatment/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/scabies/treatment/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/scabies/treatment.html - Scabies-Itch Mite Rash.
https://www.seattlechildrens.org/conditions/a-z/scabies-itch-mite-rash/ - Scabies: Tips for managing.
https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/scabies-self-care - Preventing Scabies.
https://www.cdc.gov/scabies/prevention/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/scabies/prevent.html - Scabies.
https://www.aocd.org/page/Scabies - Scabies.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4567-scabies
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Arva M Bhavnagarwala
- Dr. Neema Shrestha is a pediatrician with a special interest in the field of neonatology. She completed her graduation in medicine at Kasturba Medical College, Diploma in Child Health at D.Y. Patil University, post graduation in Pediatrics at Nepal Medical College and Fellowship in Neonatology at Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi. Dr. Shrestha has an overall experience of five years and currently works at NICU in Grande International Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal.
 Dr. Neema Shrestha is a pediatrician with a special interest in the field of neonatology. She completed her graduation in medicine at Kasturba Medical College, Diploma in Child Health at D.Y. Patil University, post graduation in Pediatrics at Nepal Medical College and Fellowship in Neonatology at Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi. Dr. Shrestha has an overall experience of five years and currently works at NICU in Grande International Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal.
Dr. Neema Shrestha is a pediatrician with a special interest in the field of neonatology. She completed her graduation in medicine at Kasturba Medical College, Diploma in Child Health at D.Y. Patil University, post graduation in Pediatrics at Nepal Medical College and Fellowship in Neonatology at Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, New Delhi. Dr. Shrestha has an overall experience of five years and currently works at NICU in Grande International Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal.
Read full bio of Sindusha MS
Read full bio of Dr. Ritika Shah
Read full bio of Dr. Joyani Das