Image: Shutterstock

Babies develop several fundamental reflexes at birth known as newborn or infant reflexes, which are generally automatic and respond to certain stimuli. Some baby reflexes, such as the symmetrical tonic neck reflex in babies (STNR), may not be present at birth but may be developed later in life. The sucking reflexiAn reflex in which babies start sucking when something touches the roof of their mouth , Moro reflexiA reflex where babies are startled by sudden noise or movement, throwing back their heads and spreading their limbs , stepping reflexiAn action when the baby tries to walk or dance in an upright position , and rooting reflexiA survival instinct that helps babies to turn their heads toward the nipple and start feeding when the corner of their mouth is touched are some other reflexes seen in newborns.
Read on to know more about STNR, its importance, and to test for it, and when you should be concerned about it.
Key Pointers
- Symmetric tonic neck reflex (STNR) involves bending and straightening of limbs along with head and neck movement.
- This reflex starts at six months and ends by 11 months.
- Sometimes, babies show STNR even after 12 months. This condition is called Retained-STNR.
- These children may prefer to lie rather than walk, have poor posture control, or walk on hands and feet.
What Is STNR?
Symmetrical or symmetric tonic neck reflex (STNR) primarily involves the bending and straightening of the limbs (legs and arms) in conjunction with the head and neck movement.
The physiological reflex displays the following attributes (1).
- When the child’s head moves forward, with the chin near the chest, their arms bend, and the legs straighten out (almost like stretching).
- When the child’s head goes backward, away from the chest, the legs bend, and arms tend to straighten out.
Image: Shutterstock
A study published in the US National Library of Medicine noted that STNR usually emerges after the age of six months and disappears by 11 months This reflex is caused by passively moving the head up and down, followed by upper extremity flexion and lower extremity extension (2). Most babies do not have this motor reflex by their first birthday when they usually may stand and walk a few steps with support.
How To Test For STNR?
You may test the presence of STNR with the following steps.
- Place the baby gently on their tummy in your hand. The baby must face forward.
- Gently move the baby’s head down so that their chin almost touches their chest. You will notice their arms bending and the legs straightening out.
- Gently move the baby’s head backward with the chin moving away from the chest. You will notice the arms straightening out while the legs start bending at the knees.
What Is The Significance Of STNR For Babies?
Many experts believe that STNR is not a primitive reflex in babies but a transitional one.
Below are some of the significant attributes of the reflex (1).
- STNR is an important part of your baby’s development since it may help them transition from lying on the floor to crawling, which itself lays the foundation for standing and walking. Hence, sometimes STNR may also be called the crawling reflex.
- STNR may play a vital role in letting the baby’s nervous system unlink the automatic movement of the head and neck from the automatic movement of the limbs. It facilitates independent yet rhythmic movement of the head and limbs during crawling.
 Quick fact
Quick factSTNR, thus, helps your baby use and move the upper and lower half of their body independent of each other. In the long run, it could facilitate better postural reflex, body balance, and eye-hand coordination during movement.
What Is STNR Integration In Babies?
STNR integration occurs when the baby’s higher brain centers inhibit the reflex and modify it to become a voluntary action (3)
. It happens as the baby’s central nervous system becomes more developed. STNR integration occurs between the ages of nine and 11 months.
What Is The Relationship Between STNR And ATNR?
The doctors at Stanford Children’s Health state that ATNR, or asymmetrical tonic neck reflex, is a primitive reflex present at birth and disappears by the age of seven months (4). Thus, STNR appears after ATNR integrates, and the two reflexes are disparate
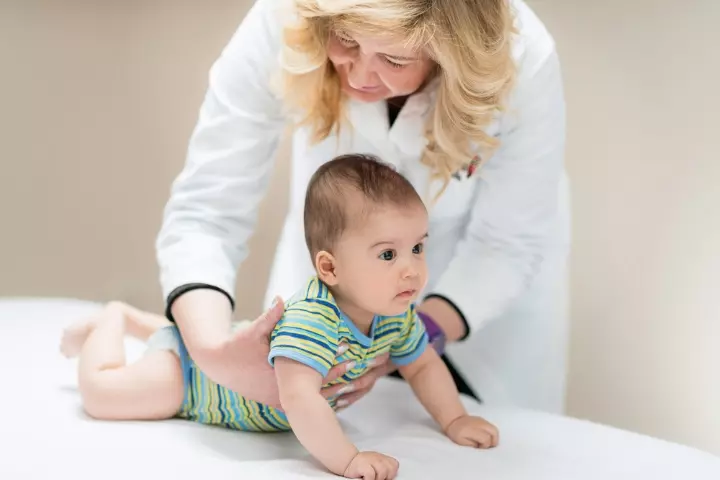
Image: Shutterstock
In ATNR, when the baby turns their head to one side, the arm on that side involuntarily stretches out. The other arm bends, and the baby may clench their fist. Some babies may also stretch the leg along with the arm while bending the other leg.
ATNR is important for developing a baby’s gross and fine motor skills, eye-tracking ability, and left-right discrimination ability (2). You may read more about ATNR here.
What Does Retained STNR Mean?
Retained STNR means that a baby displays STNR even after attaining the age of 12 months.
You may test the presence of STNR. The following signs may also indicate retained STNR in a one-year-old and can affect child development.
- Prefers lying on the floor most of the time instead of attempting to stand or walk
- Prefers scooting or dragging the body while sitting
- Loses balance and often falls while crawling
- Seems to have poor body posture control
- Walks on hands and feet instead of walking on feet while using hands to take support from objects
You may wait for a few weeks since it is often normal for STNR to integrate a bit later in some babies. However, if retained STNR persists for a month or your baby seems to display general neurodevelopmental delays, speak to a pediatrician for further assessment.
What Are The Long-Term Effects Of Retained STNR?
Retained STNR indicates poor integration of reflexes by the brain centers, indicating possible shortcomings or problems in the development of the baby’s central nervous system.
The following long-term effects may occur due to retained STNR (1).
- W-shaped sitting position where legs are spread outwards
- Awkward gait
- Difficulty in sitting still
- Hunched posture
- Frequent neck pain or body pain due to tensed muscles
- Difficulty reading, writing, and viewing objects due to poor head posture
 Quick fact
Quick fact
Image: Shutterstock
Babies with retained STNR may have other retained primitive reflexes. Therefore, it is likely that the baby may have been diagnosed already for developmental delay and could be receiving the necessary treatment. If your baby has attained all other developmental milestones, has no retention of other primitive reflexes, and displays good cognitive function, chances are it is only a case of delayed STNR integration. Nevertheless, do get your baby assessed by a pediatrician for early diagnosis of any possible developmental delay.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What happens if babies’ ATNR reflex doesn’t go away?
If the ATNR reflex doesn’t go away on time, it may cause poor eye tracking, difficulty in bilateral coordination, reading difficulties, and problems with telling the time. Retained ATNR may also lead to physical health problems such as spinal deformitiesiDisorders that give unnatural curvatures to the spine (5).
2. How long does tonic neck reflex last in babies?
Tonic neck reflex usually lasts until babies are five to seven months old (4).
3. Is symmetric tonic neck reflex beneficial for babies with special needs?
STNR is a primitive reflex that strengthens the back and neck muscles and supports good posture to help babies transition from lying to crawling. While the reflex is beneficial for babies, its delayed integration or retention, especially in babies with special needs, may have detrimental effects on their motor development.
4. What activities can I do with my baby to encourage symmetric tonic neck reflex?
Tummy time, crawling, push-pull, rocking back and forth, bear walks, and playing wheelbarrow are some activities to encourage the development and integration of STNR in babies (6).
Symmetric tonic neck reflex for babies occurs when they bend and straighten their limbs along with their head and neck. This reflex helps babies transition from lying on the floor to crawling. It is also supposed to help babies have better posture, hand-eye coordination, and body balance. Usually, STNR disappears by the age of 11 months. However, sometimes babies prefer to lie rather than crawl, lose balance, and have poor body control. These may be the signs of retained STNR, which may later cause awkward gait or hunched posture. Consult your pediatrician if you notice these signs in your baby.
Infographic: Possible Signs Of Retained STNR In Babies
STNR is an infant’s transitional reflex that helps the baby crawl. It typically emerges when the baby is 9 to 11 months old and goes away by 12 months. However, retained STNR is indicated if the baby continues to exhibit STNR signs after 12 months. Check out the infographic below to learn more about retained STNR.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntaxIllustration: What Is Symmetric Tonic Neck Reflex In Babies?

Image: Dalle E/MomJunction Design Team
The symmetric tonic neck reflex is a precursor to crawling. Here is a video explaining this reflex and how it works for babies. Watch it to better understand the importance of this reflex.
References
1. Symmetrical Tonic Neck Reflex (STNR); Rhythmic Movement Training International
2. Cristine K. Arcilla and Renato C. Vilella, Tonic Neck Reflex; U.S. National Library of Medicine
3. Primitive Motor Reflexes & Their Impact on a Child’s Function; Tools to Grow
4. Newborn Reflexes; Stanford Children’s Health
5. Ewa Z. Gieysztor et al.; Persistence of primitive reflexes and associated motor problems in healthy preschool children; NCBI
6. Symmetric Tonic Neck Reflex; Neurodevelopmental movement
7. Ewa Z. Gieysztor et al.;Persistence of primitive reflexes and associated motor problems in healthy preschool children; NCBI
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Dur Afshar Agha
Read full bio of Dr Bisny T. Joseph
Read full bio of Rohit Garoo
Read full bio of Shinta Liz Sunny